Description of fluorescent lamp
Fluorescent lamps (LL) have been on the market for a long time. Manufacturers did not follow the standards for a long time, which, due to the simplicity of the design, had practically no effect on the quality of lighting fixtures. Now the LL market has become manageable and modern products meet certain standards. They are able to provide the desired luminous flux and at the same time are distinguished by economical energy consumption.
What is a fluorescent lamp
The low efficiency of traditional incandescent lamps has long been a headache for electrical equipment manufacturers. The problem of saving energy became more and more urgent and in 1936 a solution was proposed. In Russia, special gas-discharge devices have appeared that can combine lighting with energy savings.
A fluorescent lamp is a design of a bulb with electrodes placed inside. The form can be any, only the composition of the gas affects the work.After a voltage is applied between the electrodes, the process of electron emission starts, which creates radiation.

However, the radiation obtained at this stage is in the ultraviolet range and is not visible to the human eye. In order for the light to become visible, the bulb is coated on top with a special compound - a phosphor.
Inside the flask is an inert gas or mercury vapor to maintain a glow discharge between the electrodes. An inert gas is a safe option because it does not enter into any interaction with the surrounding space. But devices with mercury vapor are extremely dangerous. Devices containing such contents must be properly disposed of and care must be taken when handling flasks.
Types of fluorescent lamps
All fluorescent lamps are usually divided into two large groups: high and low pressure devices.
High pressure devices are often used in street lamps. They are capable of producing a strong luminous flux, but the color rendering parameters are at a low level. On sale you can find lamps with different levels of light output and shades of glow. They are used for powerful lighting, as decorative lighting for buildings.

Low pressure LLs are more common. They are widely used in everyday life and at work. Most often, the models have the form of small cylinders. Such electrical appliances have ballasts, which reduces the pulsation factor and makes the glow more uniform. A component is a small circuit placed in the base of a light bulb.
Marking and dimensions
Each LL has its own technical characteristics that determine its use. Usually, all information about the device is encrypted in the label.
The designation begins with the letter L, which means a lamp. Then comes the letter designation of the shade.
| Marking | Meaning |
|---|---|
| D | day glow |
| B | White light |
| HB | cold white |
| TB | warm white |
| E | natural light |
| XE | cool natural light |
| G, K, Z, F, R | various shades depending on the type of gas used and the phosphor used |
Sometimes in the marking you can find the designation Ts or TsT, which indicates an improved color rendering of the phosphor. For example, the designation LDC is typical for a fluorescent lamp with improved color rendering.
The following are digital designations that comply with global standards. These are three digits, the first of which determines the color rendering quality, and the rest indicates a specific color temperature. The larger the first number, the better the color reproduction. An increase in the remaining numbers indicates a colder glow.

LL devices vary in size. The designation "TX" is responsible for the dimensions, where X is a specific size parameter. In particular, T5 means 5/8 inch diameter, and T8 means 8/8 inch.
Plinths can be pin or threaded. In the first case, the designation is G23, G24, G27 or G53. The number indicates the distance between the pins. Threaded bases are available with E14, E27 and E40 markings. Here the number defines the diameter of the thread.
Additionally, the lamp indicates the supply voltage and launch method. If the box has the designation RS, then no additional equipment is required for operation. All the necessary elements are already built into the plinth.
Power and spectrum
In order for the light source to work properly, it must be connected to a 220 V network with a frequency of 50 Hz. Deviation can adversely affect the stability of lighting, significantly reduce the service life.
Voltage fluctuations can change the power of an electrical device, reducing its efficiency. Even the most powerful lamp with a lack of voltage will shine weakly.
A must-see: fluorescent lamps are banned from 2020.
Modern LL have almost any shades. The color temperature spectrum varies from classic warm to daylight. By shades, each lamp is marked accordingly.
Separately, it is worth considering lighting devices with ultraviolet glow. They are marked with the LUF mark, while reflex devices of blue color are marked LSR. UV lamps are used for bactericidal treatment premises.
Most fluorescent lamps produce a flux that is close to ordinary sunlight along its length. You can see the similarity between the spectra in the picture below.
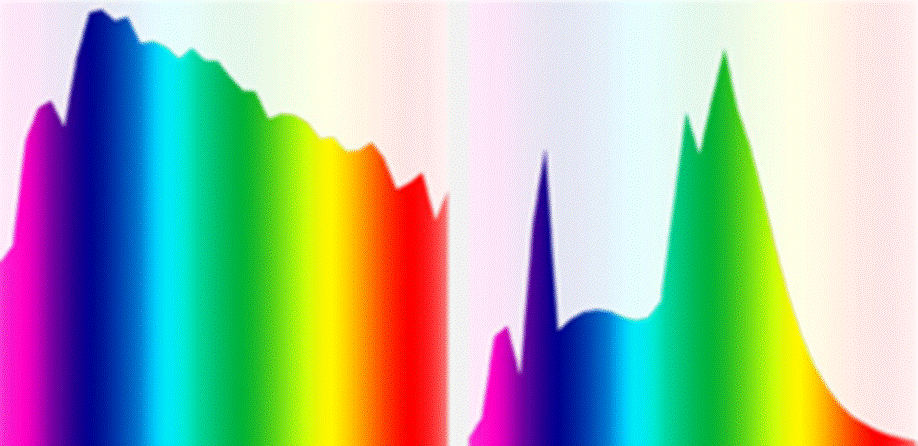
On the left is the spectrum of sunlight, on the right is the spectrum of a high-quality fluorescent lamp. The light of the sun has a more even characteristic, but the similarity is definitely observed. LL has a pronounced peak in the green region, while there is a drop in the red region.
It has been scientifically proven that the closer the light of an artificial source is to natural light, the healthier it is. For this reason, fluorescent lamps are preferred over LED fixtures.
What areas are used
Fluorescent lamps can effectively illuminate large areas while significantly improving indoor conditions, reducing energy costs, and extending the life of the lighting system.
Devices with built-in electronic ballast and E27 or E14 screw bases are used in everyday life as an effective replacement incandescent lamps. They are able to provide the necessary luminous flux, guarantee stability and no flicker. In this case, the hum is completely absent. They are used in apartments, houses, shopping malls, schools, hospitals, banks, etc.

Specifications
The technical characteristics of a particular lighting device are encrypted in the marking and indicated on the packaging. This is information about lamp power, base type, dimensions, color temperature, service life.
Most modern luminescent devices can work 8-12 thousand hours. The indicator depends on the type and size of the device.
Efficiency is expressed as 80 lm/W, which is significantly more than traditional incandescent lamps. During operation, a moderate amount of heat is released, the devices are resistant to wind, able to function stably at temperatures from +5 to +55 ° C. If a heat-resistant coating is present, the instrument can be used at +60 °C.
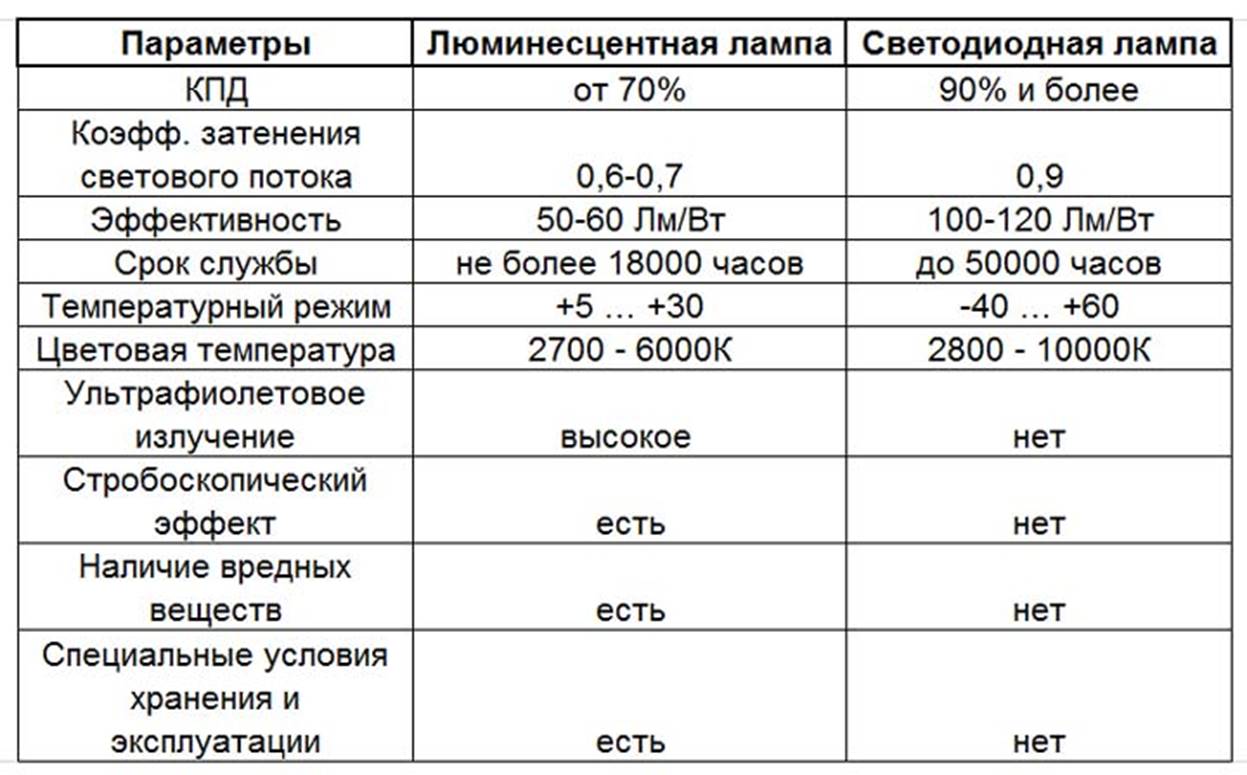
The color temperature is usually between 2700 and 6000K. The efficiency can be up to 75%.
How does the lamp work
The principle of operation of any fluorescent lamp includes the supply of voltage to the electrodes located inside the bulb.A glow discharge occurs between the electrodes, which is supported by an inert gas or mercury vapor inside the flask.
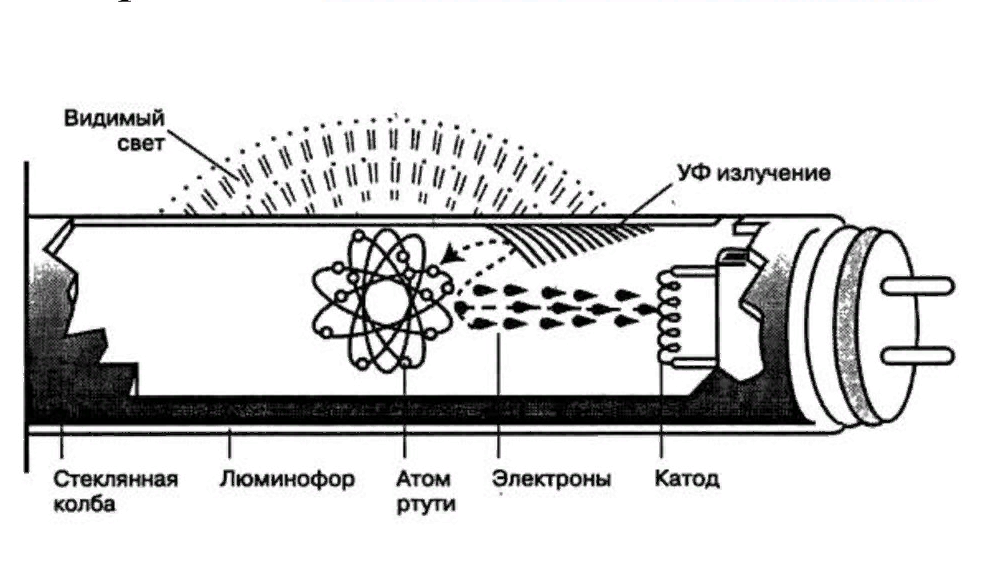
The glow discharge generates radiation in the ultraviolet range, which, through the phosphor deposited on the flask, turns into visible light of the desired shade.
For ultraviolet radiation, discharge lamps. Ordinary glass does not transmit ultraviolet, so special quartz glass is used to make the flask. There is no phosphor coating in this case. Devices are widely used in solariums and for disinfection of premises.
Why do you need a choke in a fluorescent lamp
The standard wiring diagram for a fluorescent lamp includes the light source itself, a starter and a choke.
Throttle is an inductor with a lamellar core. It plays the role of a ballast that stabilizes the voltage and prevents the lamp from quickly becoming unusable.
The starter, when turned on, receives a significant voltage, several times higher than that required for the lamp. The inductor reduces this voltage and only then applies it to the contacts of the lighting device.
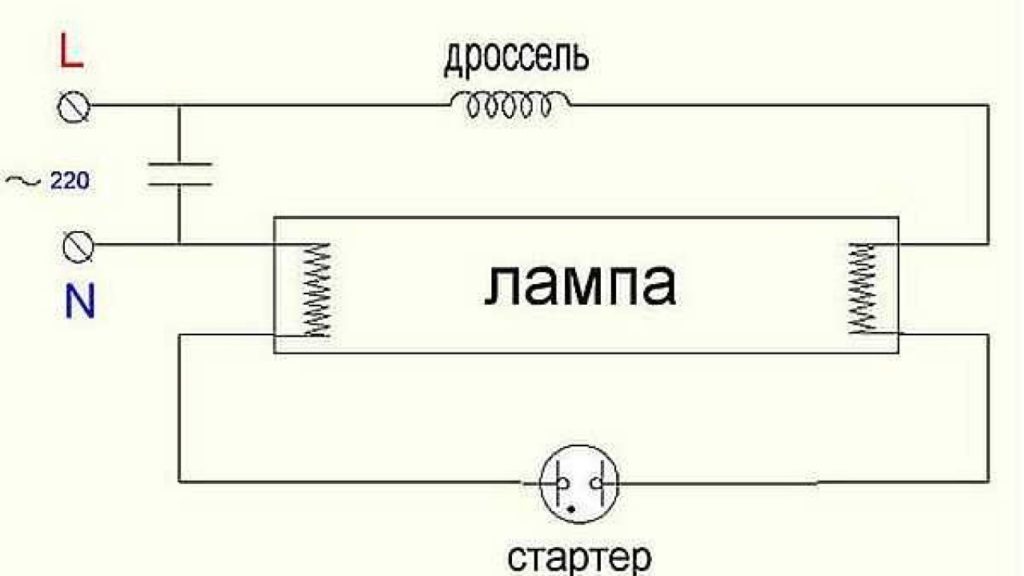
The circuit can be supplemented with a capacitor connected parallel to the power supply, which greatly improves system stability, extends the service life and reduces flicker.
How to choose
When choosing a fluorescent lamp, you need to pay attention to:
- temperature mode of use;
- voltage;
- the size;
- the strength of the light flux;
- lighting temperature.
In everyday life, devices with a threaded base and minimal flicker rates are effective.

Hallways need strong lighting, so choose lamps with an intense luminous flux. But in the bedroom or living room, compact devices with soft subdued light are appropriate.
In the kitchen, it is better to use multi-level lighting, including general and local appliances. It is advisable to select warm shades with a power of at least 20 watts.
Lamp recycling
Fluorescent lamps contain substances harmful to the environment, so waste disposal must be taken as responsibly as possible.
One lamp can contain about 70 mg of mercury, which is quite dangerous. However, there are a lot of such lamps in landfills, this is a serious problem.
The ingress of mercury into the human or animal body quickly provokes poisoning. It is forbidden to store faulty lamps in the house for a long time due to the likelihood of mechanical damage to the bulb, followed by leakage of harmful substances.

- All lamps are collected and stored in special containers.
- With the help of a press, the devices are crushed.
- The resulting crumb is sent to the heat treatment chamber.
- Harmful substances enter the filter, where they remain.
Sometimes gases are exposed to liquid nitrogen and solidify. The resulting mercury is reused.
Advantages and disadvantages of lamps
Like other light sources, fluorescent lamps have advantages and disadvantages that should be taken into account.




