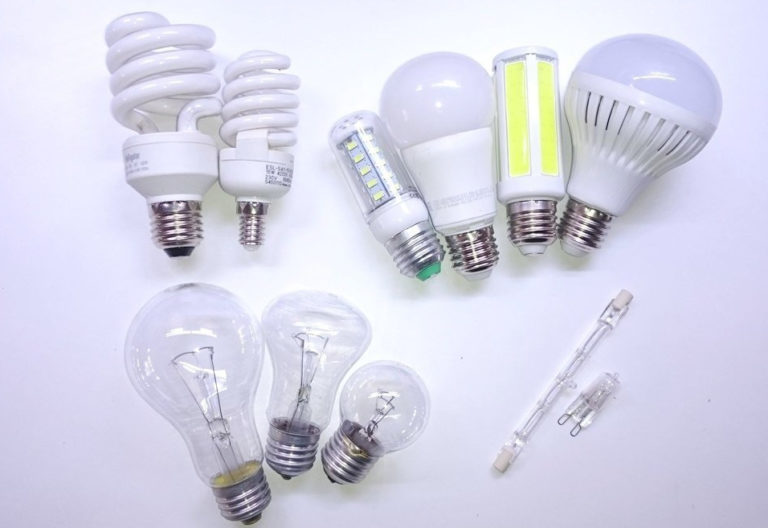
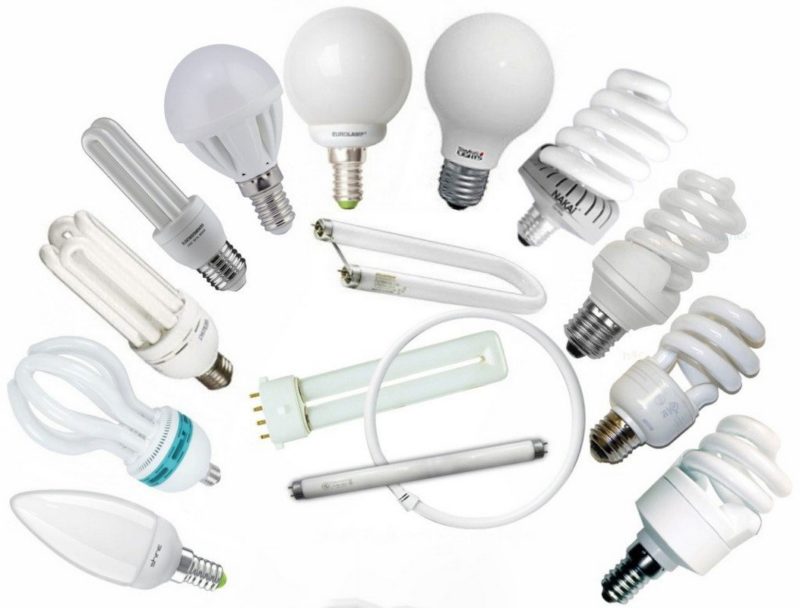
Varieties of energy-saving lamps
Every owner of an apartment, house or business strives to save as much as possible on energy consumption. One of the best options may be to replace incandescent lamps (LN) with energy-saving devices. The only thing you have to do is to choose the type of light bulbs, taking into account their characteristics and purpose.
To choose from a variety of energy-saving lamps, you need to study their principle of operation, power ratings, advantages and disadvantages, as well as possible harm to health. It is better to give preference to high-quality models, since cheap analogues often do not correspond to the declared characteristics and quickly burn out.
What are energy saving lamps
Varieties are called energy-saving fluorescent lamps. They consist of a base and a flask. Inside are tungsten electrodes coated with activating substances: strontium, calcium and barium.These lamps must not be disposed of with normal household waste. For this, there are special reception points.

Inside the lamp is an inert gas or mercury, which turns into steam during the heating process. When switched on, a charge appears between the electrodes. The resulting radiation is in the ultraviolet range of the spectrum. To convert it into visible light, the inner surface of the flask is coated with a phosphor.
Types of energy saving lamps
Energy-saving lamps come in several types. Each of them has its own purpose. For example, halogen lamps are rarely installed in household appliances due to a number of disadvantages. So, they get very hot, which is not always satisfactory. At the same time, they have a number of advantages, and they are easy to pick up for any type of ceiling.
Fluorescent
Energy-saving lamps are divided into 2 types - compact and standard (linear). Both devices have a lot in common. In both cases, the design includes a sealed glass flask with gas (neon or argon) inside. There is also a small amount of mercury. The electrodes are connected with regulatory apparatus.
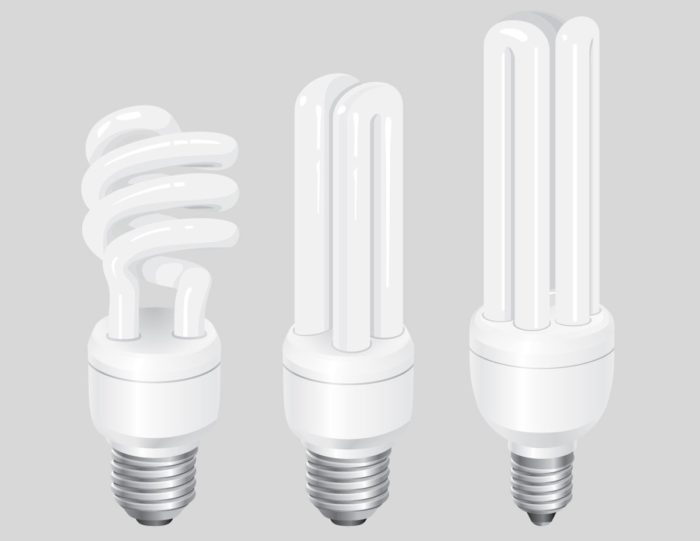

Mercury vapors, mixing with gases, emit ultraviolet radiation. To convert the UV spectrum to daylight, the inside of the flask is treated with a phosphor. The difference between a compact lamp and a fluorescent lamp is as follows:
- the size. U-shaped or spiral-shaped have the same functions, but a more complex, twisted shape to reduce size;
- installation. Linear analogues are mounted as separate elements, fixed in the lamp housing. Compact products are installed in a base or flask.
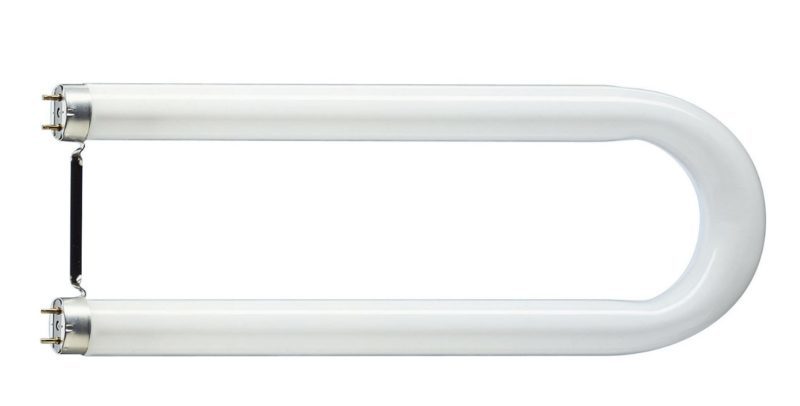

Since this view has the same functions as incandescent lamps, they are easily installed in any fixtures (chandeliers and sconces). Linear light bulbs are called because of the shape, since their base is a straight tube. In the people they are called "fluorescent lamps". On sale you can find products of different shapes - double, U-shaped and ring. They don't have a plinth. Metal rods are installed on the tubes, which are connected to the network with terminals.
continuous action
This type of energy-saving light bulbs is the least familiar to customers. These lamps are the best color reproductionwhile having lower light output. The main advantage is continuous spectrum radiation. Such models are among the safest.
Special color
Such energy-saving lamps are divided into:
- ultraviolet;
- with colored phosphor;
- with pink glow.

This type of light bulbs is not used to illuminate rooms. Their main purpose is to create a festive atmosphere. Such lamps can be found in exhibition and concert halls, clubs, restaurants, light shows and playgrounds.
The glow surface of this type of lamp is larger than that of other LNs. This creates a more comfortable and uniform lighting. On the shelves of shops you can find light bulbs of blue, green, yellow and red colors. They work from a 220 V network, like ordinary ones. One of the advantages of such lamps is that even turned off, they decorate the room.
LED
Due to the energy-saving properties of LED crystals, they were previously used in radio engineering as indicators. Later, technology improved, and LEDs began to be used as super-bright components in backlight circuits.They have found application in almost all areas.

The design consists of a bulb, inside of which there are getinaks, a bar, LEDs and a driver. The body is elongated, "corn" or spot. The risk of mechanical damage is reduced due to the polycarbonate housing.
The lamps are connected to a 220 V network without the need for ballasts. The narrow shape of diode lamps allows them to be combined into small and large groups. According to the places of installation are classified into:
- office and household;
- industrial;
- for installation in street spotlights;
- automotive;
- phytolamps;
- for growing plants.
Linear devices are often used for lighting in landscape design. Here it is better to choose lamps with high degree of protection – IP67 or IP65. The shape can be tubular or in the form of a spotlight. If it is a room with a standard climate, an IP20 level will do.
LED light bulbs best selling. Of all lamp types, they consume the least energy, require no special disposal, do not emit heat, and last up to 100,000 hours depending on the model. Quality devices can withstand voltage surges and sudden temperature changes. Almost the only disadvantage of these lamps is the high price.
The principle of operation of an energy-saving lamp
Different types of energy-saving devices work according to different principles. If it is a fluorescent light bulb, inside the bulb is an inert gas mixed with mercury vapor. As mentioned above, the inside of the tube is coated with a phosphor. It is necessary to create a color temperature and a glow spectrum.
The case contains a voltage converter (driver) that performs a ballast function. When voltage is applied to the lamp, the driver creates a breakdown of the gas gap between the electrodes.
Spirals heat up, which increases the emissivity of the electrodes and the evaporation of mercury. After a few seconds, a gas discharge occurs in the flask. After that, the driver goes into ballast mode. Voltage and current are stabilized at the optimum level. Mercury vapor emits ultraviolet radiation during discharge. It is absorbed by the phosphor, which will begin to emit light in the visible part of the spectrum.
Application area
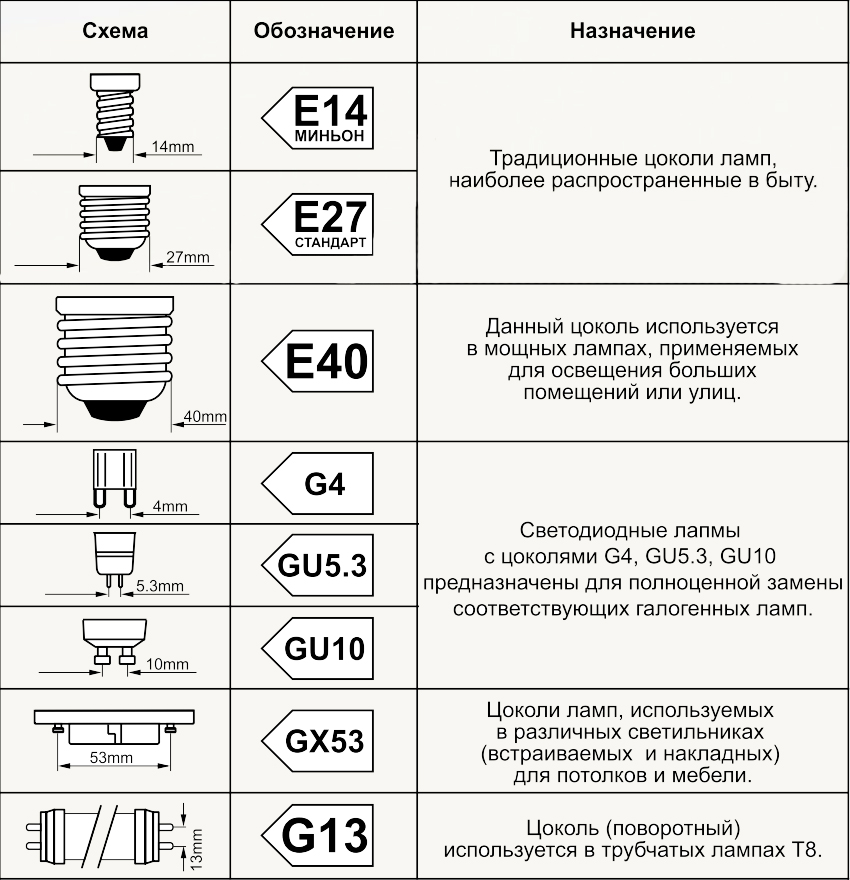
According to the type of base, fluorescent lamps are marked as follows:
- G53. Produced in a sealed case and designed for rooms with high humidity. Often mounted in plasterboard or stretch ceilings;
- 2D. Used for decoration, for built-in lighting in showers;
- G24. Are intended for installation in household fixtures and on industrial objects;
- 2G7 and G23. Installed in wall lamps with special holes.
Lamps with base E14, E40, E27 can be screwed into cartridges, replacing LN. They are large and do not fit all fixtures. The advantage that distinguishes them from other light bulbs is a better color rendering.
Meet:
- with colored phosphors. They are used for artistic lighting, advertising signs, citylights and inscriptions;
- with ultraviolet radiation. Suitable for lighting dark areas, disinfection in hospitals, entertainment events;
- with pink glow. It is actively used in the meat industry to give the meat on display a marketable appearance.
LED lamps are often used for household, industrial and street lighting. Products emit light in one direction, which makes them indispensable for creating a directional flow. They are purchased for art galleries and museums, as they do not emit ultraviolet radiation.
Power
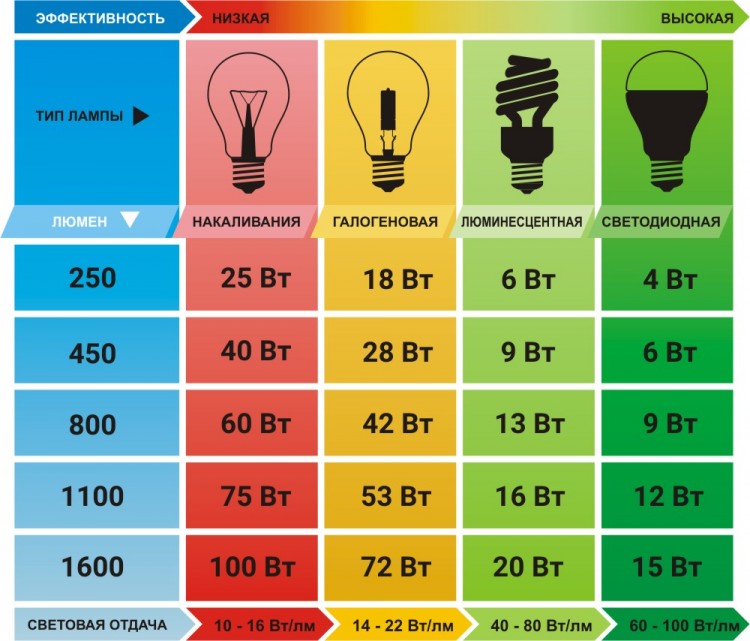
The energy consumption of different types of lamps varies, depends on the power of the lamp and is measured in watts. Below is a comparison table:
| Lm - luminous flux. | Type of lamp and its power | |||
| LED | incandescent | Fluorescent | Halogen | |
| 3040 | 26 | 200 | 45 | 120 |
| 2160 | 22 | 150 | 36 | 90 |
| 1700 | 18 | 120 | 24 | 72 |
| 1340 | 12 | 100 | 20 | 60 |
| 710 | 8 | 60 | 12 | 36 |
| 415 | 4 | 24 | 8 | 24 |
| 220 | 2 | 12 | 6 | 15 |
Harm of energy-saving lamps
Some types of energy-saving lamps have a drawback - they contain mercury vapor. Their number is minimal and not capable of much harm to a person. In order for the harm to become tangible, you need to break many fluorescent lamps at the same time in a small room.

Harm to humans can be avoided if properly used and dispose of products. LEDs are completely harmless and do not require special disposal.
How to choose lamps
When choosing, you need to consider the following:
- light temperature and light color. For office premises, it is advisable to buy products with cold shades and temperatures up to 6500 K. If this is a children's room, it is recommended to purchase lamps with natural shades up to 4200 K;
- power. To determine the power of the LN, it is divided by 5. For example, if the LN has a power of 100 V, the energy-saving one will be 20 V. But such calculations are not correct for all types of devices;
- the form. Consideration should be given to the design of the room or fixture;
- lifetime.LED lamps are the most durable;
- guarantee. The maximum warranty period is up to 3 years for LED products.
Related video: What energy-saving lamps really help save
Advantages and disadvantages of lamps
The advantages of energy-saving lamps include the following:
- up to 100,000 hours of continuous operation;
- profitability;
- expensive models do not lose brightness during operation;
- LED lamps practically do not heat up;
- the ability to choose any light shade;
- guarantee;
- a large number of forms.
Flaws:
- the presence of harmful vapors in the flask, which is why the light bulbs must be taken to specialized collection points;
- high price;
- with frequent switching on and off, the service life is reduced;
- brightness increases gradually after switching on.

Conclusion
When choosing an energy-saving lamp, a number of characteristics should be taken into account: power, color temperature, susceptibility to damage, installation features. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which plays a key role in choosing a light bulb.