What is light polarization and its practical application
Polarized light differs from standard light in its distribution. It was discovered a long time ago and is used both for physical experiments and in everyday life to perform some measurements. Understanding the phenomenon of polarization is not difficult, this will allow you to understand the principle of operation of some devices and find out why, under certain conditions, light does not propagate as usual.

What is light polarization
The polarization of light proves that light is a transverse wave. That is, we are talking about the polarization of electromagnetic waves in general, and light is one of the varieties, the properties of which are subject to general rules.
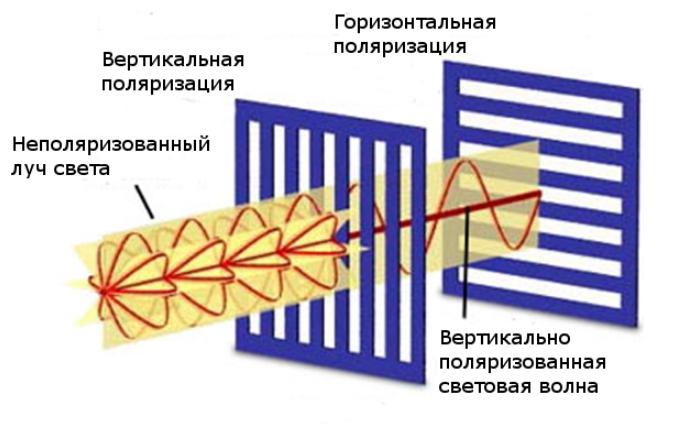
Polarization is a property of transverse waves, the oscillation vector of which is always perpendicular to the direction of propagation of light or something else.That is, if you select from the light rays with the same polarization of the vector, then this will be the phenomenon of polarization.
Most often, we see unpolarized light around us, since its intensity vector moves in all possible directions. To make it polarized, it is passed through an anisotropic medium, which cuts off all oscillations and leaves only one.
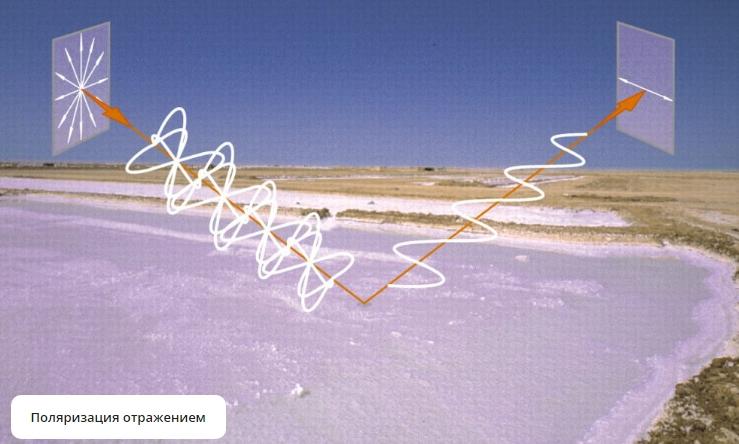

Who discovered the phenomenon and what does it prove
The concept under consideration was used for the first time in history by a famous British scientist I. Newton in 1706. But another researcher explained its nature - James Maxwell. Then the nature of light waves was not known, but with the accumulation of various facts and the results of various experiments, more and more evidence of the transverseness of electromagnetic waves appeared.
The first to conduct experiments in this area was a Dutch researcher Huygens, this happened in 1690. He passed light through a plate of Icelandic spar, as a result of which he discovered the transverse anisotropy of the beam.
The first evidence of the polarization of light in physics was obtained by a French researcher E. Malus. He used two plates of tourmaline and eventually came up with a law named after him. Thanks to numerous experiments, the transverseness of light waves was proved, which helped to explain their nature and propagation features.
Where does the polarization of light come from and how to get it yourself
Most of the light we see is not polarized. Sun, artificial lighting - a luminous flux with a vector oscillating in different directions, spreads in all directions without any restrictions.
Polarized light appears after it has passed through an anisotropic medium, which can have different properties. This environment removes most of the fluctuations, leaving the only thing that provides the desired effect.
Most often, crystals act as a polarizer. If previously mainly natural materials were used (for example, tourmaline), now there are many options for artificial origin.
Also, polarized light can be obtained by reflection from any dielectric. The bottom line is that when luminous flux it is refracted at the junction of two media. This is easy to see by placing a pencil or a tube in a glass of water.
During the phenomenon of refraction of light, part of the rays is polarized. The degree of manifestation of this effect depends on the location light source and the angle of its incidence relative to the point of refraction.
As for the methods for obtaining polarized light, one of three options is used regardless of the conditions:
- Prism Nicolas. It is named after the Scottish explorer Nicolas William who invented it in 1828. He conducted experiments for a long time and after 11 years was able to get a finished device, which is still used unchanged.
- Reflection from a dielectric. Here it is very important to choose the optimal angle of incidence and take into account the degree refraction (the greater the difference in the light transmission of the two media, the more the rays are refracted).
- Using an anisotropic environment. Most often, crystals with suitable properties are selected for this. If you direct a light flux at them, you can observe its parallel separation at the output.
Polarization of light upon reflection and refraction at the interface of two dielectrics
This optical phenomenon was discovered by a physicist from Scotland David Brewster in 1815. The law he derived showed the relationship between the indicators of two dielectrics at a certain angle of incidence of light. If we choose the conditions, then the rays reflected from the interface of two media will be polarized in a plane perpendicular to the angle of incidence.
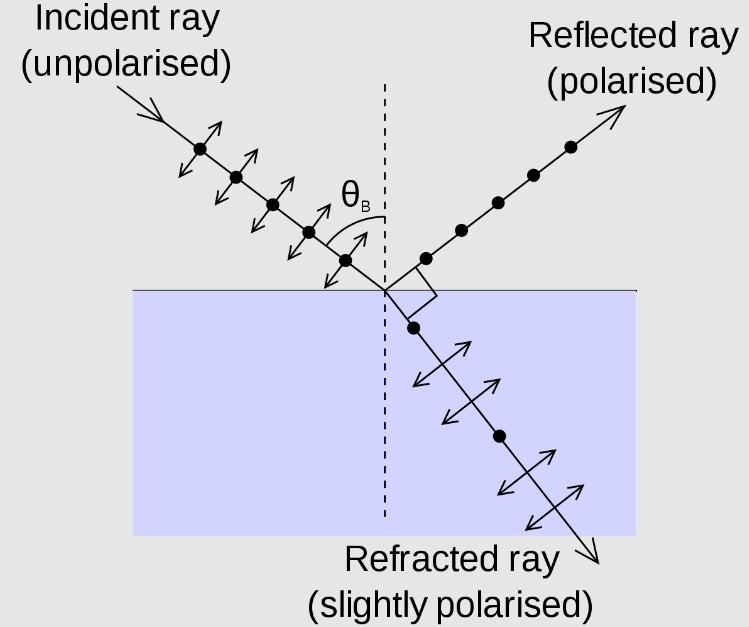
The researcher noted that the refracted beam is partially polarized in the plane of incidence. In this case, not all the light is reflected, part of it goes into the refracted beam. Brewster angle is the angle at which reflected light completely polarized. In this case, the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other.
To understand the reason for this phenomenon, you need to know the following:
- In any electromagnetic wave, the oscillations of the electric field are always perpendicular to the direction of its movement.
- The process is divided into two stages. In the first, the incident wave causes the molecules of the dielectric to excite, in the second, refracted and reflected waves appear.
If one plastic of quartz or other suitable mineral is used in the experiment, intensity plane polarized light will be small (about 4% of the total intensity). But if you use a stack of plates, you can achieve a significant increase in performance.
By the way! Brewster's law can also be derived using Fresnel's formulas.
Polarization of light by a crystal
Ordinary dielectrics are anisotropic and the characteristics of light when it hits them depend mainly on the angle of incidence. The properties of the crystals are different, when light hits them, you can observe the effect of double refraction of the rays.This manifests itself as follows: when passing through the structure, two refracted beams are formed, which go in different directions, their speeds also differ.
Most often, uniaxial crystals are used in experiments. In them, one of the refraction beams obeys standard laws and is called ordinary. The second is formed differently, it is called extraordinary, since the features of its refraction do not correspond to the usual canons.
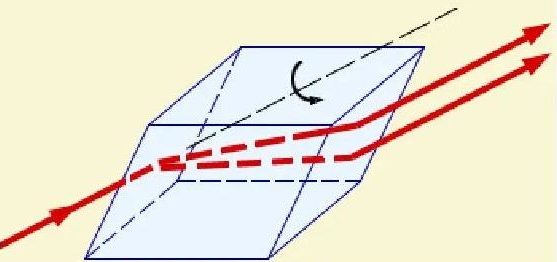
If you rotate the crystal, then the ordinary beam will remain unchanged, and the extraordinary one will move around the circle. Most often, calcite or Icelandic spar are used in experiments, as they are well suited for research.
By the way! If you look at the environment through the crystal, then the outlines of all objects will split in two.
Based on experiments with crystals Étienne Louis Malus formulated the law in 1810 the year that received his name. He deduced a clear dependence of linearly polarized light after its passage through a polarizer made on the basis of crystals. The intensity of the beam after passing through the crystal decreases in proportion to the square of the cosine of the angle formed between the plane of polarization of the incoming beam and the filter.
Video lesson: Polarization of light, physics Grade 11.
Practical application of light polarization
The phenomenon under consideration is used in everyday life much more often than it seems. Knowledge of the laws of propagation of electromagnetic waves helped in the creation of various equipment. The main options are:
- Special polarizing filters for cameras allow you to get rid of glare when taking pictures.
- Drivers often use glasses with this effect, as they remove glare from the headlights of oncoming vehicles.As a result, even high beams cannot dazzle the driver, which improves safety.The absence of glare is due to the effect of polarization.
- The equipment used in geophysics makes it possible to study the properties of cloud masses. It is also used to study the features of the polarization of sunlight when passing through clouds.
- Special installations that photograph cosmic nebulae in polarized light help to study the features of the magnetic fields that arise there.
- In the engineering industry, the so-called photoelastic method is used. With it, you can clearly determine the stress parameters that occur in the nodes and parts.
- Equipment used when creating theatrical scenery, as well as in concert design. Another area of application is showcases and exhibition stands.
- Devices that measure the level of sugar in a person's blood. They work by determining the angle of rotation of the plane of polarization.
- Many food industry enterprises use equipment capable of determining the concentration of a particular solution. There are also devices that can control the content of proteins, sugars and organic acids through the use of polarization properties.
- 3D cinematography works precisely through the use of the phenomenon considered in the article.
By the way! Familiar to all liquid crystal monitors and TVs also work on the basis of a polarized stream.
Knowing the basic features of polarization allows you to explain the many effects that occur around. Also, this phenomenon is widely used in science, technology, medicine, photography, cinema and many other areas.
