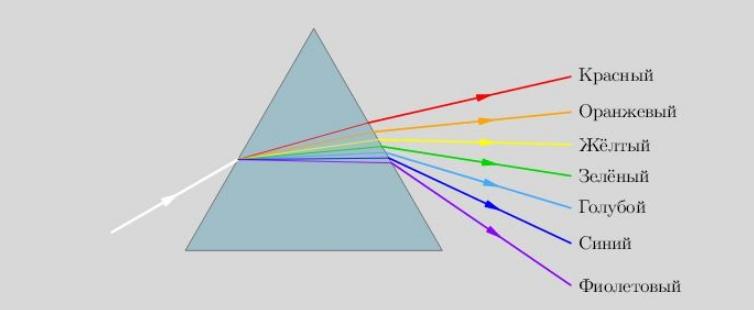
The formula for the law of refraction of light - general and particular cases
The law of refraction of light is used in various fields and allows you to determine how the rays will behave when they hit from one medium to another. It is easy to understand the features of this phenomenon, the reasons for its occurrence and other important nuances. It is also worth understanding the types of refraction, as this is of great importance in the calculation and practical use of the principles of the law.
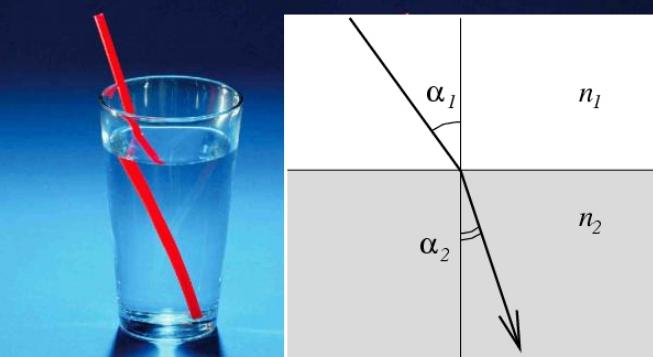
What is the phenomenon of refraction of light
Almost everyone is familiar with this phenomenon, as it is widely encountered in everyday life. For example, if you look at the bottom of a reservoir with clear water, it always seems closer than it really is. Distortion can be observed in aquariums, this option is familiar to almost everyone.But to understand the issue, it is necessary to consider several important aspects.
Reasons for refraction
Here, the characteristics of the different media through which the light flux passes are of decisive importance. Their density most often differs, so light travels at different speeds. This directly affects its properties.
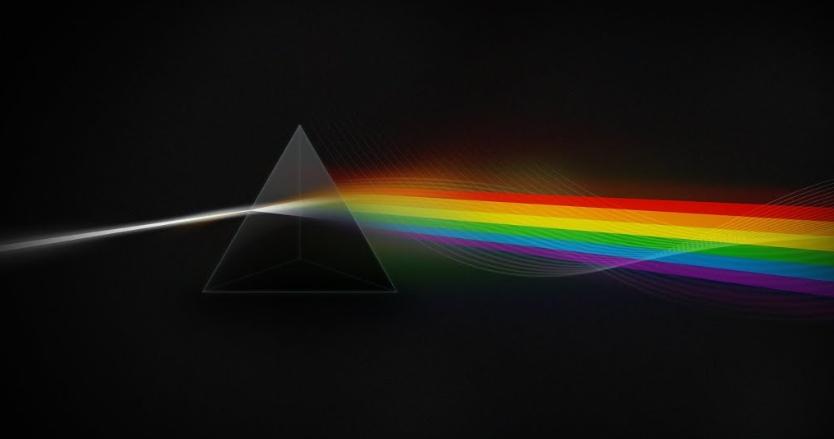

When moving from one medium to another (at the point of their connection), the light changes its direction due to differences in density and other features. The deviation can be different, the greater the difference in the characteristics of the media, the greater the distortion in the end.
By the way! When light is refracted, some of it is always reflected.
Real life examples
You can meet examples of the phenomenon under consideration almost everywhere, so everyone can see how refraction affects the perception of objects. The most typical options are:
- If you place a spoon or a tube in a glass of water, you can see how visually the object ceases to be straight and deviates, starting from the border of two environments. This optical illusion is used as an example most often.
- In hot weather, the puddle effect often occurs on the pavement. This is due to the fact that in the place of a sharp temperature drop (near the earth itself), the rays are refracted so that the eyes see a slight reflection of the sky.
- Mirages also appear as a result of refraction. Everything is much more complicated here, but at the same time, this phenomenon occurs not only in the desert, but also in the mountains and even in the middle lane. Another option is when objects that are behind the horizon line are visible.Mirage is one of the wonders of nature, which occurs precisely because of the refraction of light.
- The principles of refraction are also used in many objects used in everyday life: glasses, magnifying glass, peepholes, projectors and slide show machines, binoculars and much more.
- Many types of scientific equipment work by applying the law in question. This includes microscopes, telescopes and other sophisticated optical instruments.
What is the angle of refraction
The angle of refraction is the angle that is formed due to the phenomenon of refraction at the interface between two transparent media with different light transmission properties. It is determined from a perpendicular line drawn to the refracted plane.
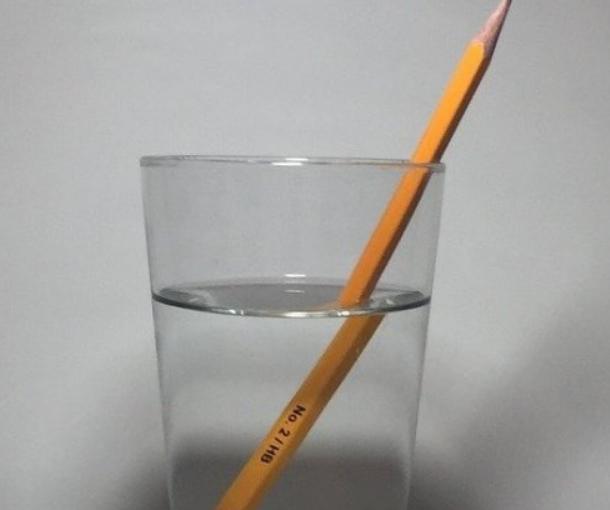

This phenomenon is due to two laws - conservation of energy and conservation of momentum. With a change in the properties of the medium, the wave speed inevitably changes, but its frequency remains the same.
What determines the angle of refraction
The indicator can vary and primarily depends on the characteristics of the two media through which the light passes. The greater the difference between them, the greater the visual deviation.
Also, the angle depends on the length of the emitted waves. As this indicator changes, the deviation also changes. In some media, the frequency of electromagnetic waves also has a great influence, but this option is not always found.
In optically anisotropic materials, the angle is affected by the polarization of light and its direction.
Types of refraction
The most common is the usual refraction of light, when, due to the different characteristics of the media, a distortion effect can be observed to one degree or another.But there are other varieties that appear in parallel or can be considered as a separate phenomenon.
When a vertically polarized wave hits the boundary of two media at a certain angle (called the Brewster angle), you can see the total refraction. In this case, there will be no reflected wave at all.
Total internal reflection can only be observed when radiation passes from a medium with a higher refractive index to a less dense medium. In this case, it turns out that the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence. That is, there is an inverse relationship. Moreover, with an increase in the angle, upon reaching certain values of it, the indicator becomes equal to 90 degrees.

If you increase the value even more, then the beam will be reflected from the boundary of two substances without passing to another medium. It is this phenomenon that is called total internal reflection.
Here you need an explanation regarding the calculation of indicators, since the formula differs from the standard one. In this case, it will look like this:
sin etc=n21
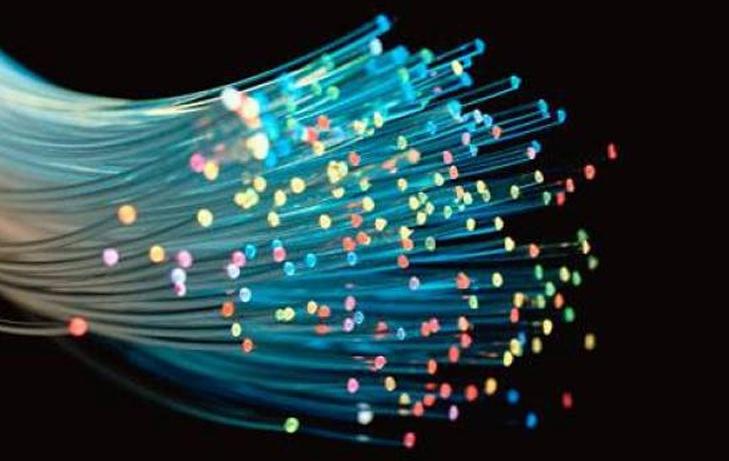
This phenomenon led to the creation of optical fiber, a material that can transmit huge amounts of information over an unlimited distance at a speed unattainable by other options. In contrast to a mirror, in this case reflection occurs without loss of energy even with multiple reflections.
Optical fiber has a simple structure:
- The light transmitting core is made of plastic or glass. The larger its cross section, the greater the amount of information that can be transmitted.
- The shell is necessary to reflect the light flux in the core so that it propagates only through it. It is important that at the point of entry into the fiber, the beam falls at an angle greater than the limit, then it will be reflected without energy loss.
- Protective isolation prevents damage to the fiber and protects it from adverse effects. Due to this part, the cable can also be laid underground.

How was the law of refraction discovered?
This discovery was made Willebrord Snellius, a Dutch mathematician, in 1621. After a series of experiments, he was able to formulate the main aspects that have remained virtually unchanged to this day. It was he who first noted the constancy of the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and reflection.
The first publication with the materials of the discovery was made by a French scientist Rene Descartes. At the same time, experts disagree, someone believes that he used the materials of Snell, and someone is sure that he independently rediscovered it.
Definition and formula of the refractive index
The incident and refracted rays, as well as the perpendicular passing through the junction of two media, are within the same plane. The sine of the angle of incidence with respect to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant value. This is how the definition sounds, which may differ in presentation, but the meaning always remains the same. The graphical explanation and formula are shown in the picture below.
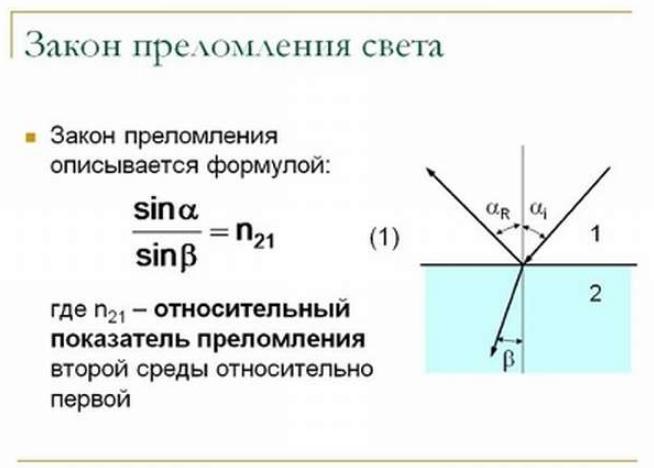
It should be noted that the indicators refractions do not have any units. At one time, when studying the physical foundations of the phenomenon under consideration, two scientists at once - Christian Huygens from Holland and Pierre de Fermat from France came to the same conclusion. According to him, the sine of incidence and the sine of refraction are equal to the ratio of the velocities in the media through which the waves pass. If light travels through one medium faster than another, then it is optically less dense.
By the way! The speed of light in a vacuum higher than any other substance.
The physical meaning of "Snell's Law"
When light passes from vacuum to any other substance, it inevitably interacts with its molecules. The higher the optical density of the medium, the stronger the interaction of light with atoms and the lower the speed of its propagation, while with increasing density, the refractive index also increases.
Absolute refraction is denoted by the letter n and allows you to understand how the speed of light changes when moving from vacuum to any medium.
Relative refraction (n21) shows the parameters of the change in the speed of light when moving from one medium to another.
The video explains the law from grade 8 physics very simply with the help of graphics and animation.
Scope of the law in technology
A lot of time has passed since the discovery of the phenomenon and practical research. The results helped to develop and implement a large number of devices used in various industries, it is worth analyzing the most common examples:
- Ophthalmic equipment. Allows you to conduct a variety of studies and identify pathologies.
- Apparatus for the study of the stomach and internal organs. You can get a clear image without introducing a camera, which greatly simplifies and speeds up the process.
- Telescopes and other astronomical equipment, due to refraction, make it possible to obtain images that are not visible to the naked eye.The refraction of light in the lenses of telescopes makes it possible to collect light at a focus, providing high-precision research.
- Binoculars and similar devices also work on the basis of the above principles. This also includes microscopes.
- Photo and video equipment, or rather its optics, use the refraction of light.
- Fiber optic lines that transmit large amounts of information over any distance.
Video lesson: Conclusion according to the law of refraction of light.
Refraction of light is a phenomenon that is due to the characteristics of different media. It can be observed at the point of their connection, the angle of deviation depends on the difference between the substances. This feature is widely used in modern science and technology.