Characteristic of RGB LED
The backlight that changes its color looks impressive. It is used for advertising objects, decorative lighting of architectural objects, during various shows and public events. One way to implement such a backlight is to use tricolor LEDs.
What is RGB LED
Ordinary light-emitting semiconductor devices have one p-n junction in one package, or they are a matrix of several identical junctions (COB technology). This allows you to get one glow color at each moment of time - directly from the recombination of the main carriers or from the secondary glow of the phosphor. The second technology gave developers ample opportunities in choosing the color of the glow, but the device cannot change the color of the radiation during operation.
The RGB LED contains three p-n junctions with different glow colors in one package:
- red (Red);
- green (Green);
- blue.
The abbreviation of the English names of each color gave the name to this type of LED.
Types of RGB diodes
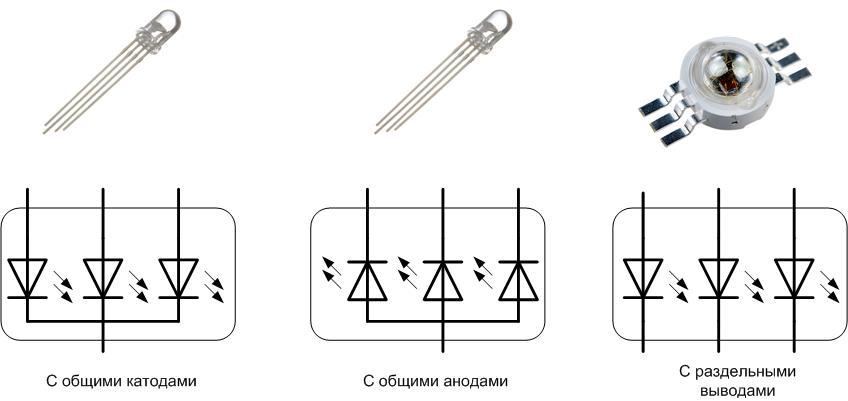
Three-color LEDs are divided into three types according to the method of connecting the crystals inside the case:
- with a common anode (have 4 outputs);
- with a common cathode (have 4 outputs);
- with separate elements (have 6 conclusions).
The way the device is controlled depends on the version of the LED.
According to the type of lens, LEDs are:
- with transparent lens;
- with frosted lens.
Clear lens RGB elements may require additional light diffusers to achieve mixed hues. Otherwise, individual color components may be visible.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of RGB LEDs is based on mixing colors. Controlled ignition of one, two or three elements allows you to get a different glow.
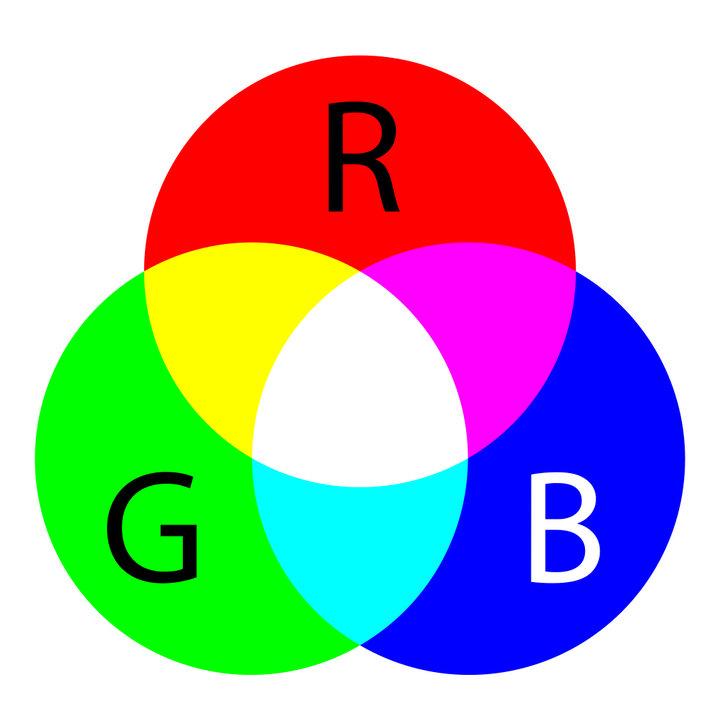
Turning on the crystals individually gives the three corresponding colors. Pairwise inclusion allows you to achieve a glow:
- red + green p-n junctions will eventually give yellow;
- blue + green when mixed gives turquoise;
- red + blue make purple.
The inclusion of all three elements allows you to get white.
Much more possibilities are given by mixing colors in various proportions. This can be done by separately controlling the brightness of the glow of each crystal. To do this, you must individually adjust the current flowing through the LEDs.

RGB LED control and wiring diagram
The RGB LED is controlled in the same way as a conventional LED - by applying a direct anode-cathode voltage and creating a current through the p-n junction.Therefore, it is necessary to connect a tricolor element to a power source through ballast resistors - each crystal through its own resistor. Calculate it can be through the rated current of the element and operating voltage.
Even when combined in the same package, different crystals can have different parameters, so they cannot be connected in parallel.
Typical characteristics for a low-power three-color device with a diameter of 5 mm are given in the table.
| Red (R) | Green (G) | Blue (B) | |
| Maximum forward voltage, V | 1,9 | 3,8 | 3,8 |
| Rated current, mA | 20 | 20 | 20 |
Obviously, the red crystal has a forward voltage that is half that of the other two. Parallel connection of elements will lead to a different brightness of the glow or the failure of one or all p-n junctions.
Permanently connected to a power source does not allow you to use the full capabilities of the RGB element. In static mode, a three-color device only performs the functions of a monochrome one, but costs much more than a conventional LED. Therefore, the dynamic mode is much more interesting, in which the color of the glow can be controlled. This is done through a microcontroller. Its outputs in most cases provide an output current of 20 mA, but this needs to be specified in the datasheet each time. Connect the LED to the output ports through a current-limiting resistor. A compromise option when powering the microcircuit from 5 V is a resistance of 220 ohms.
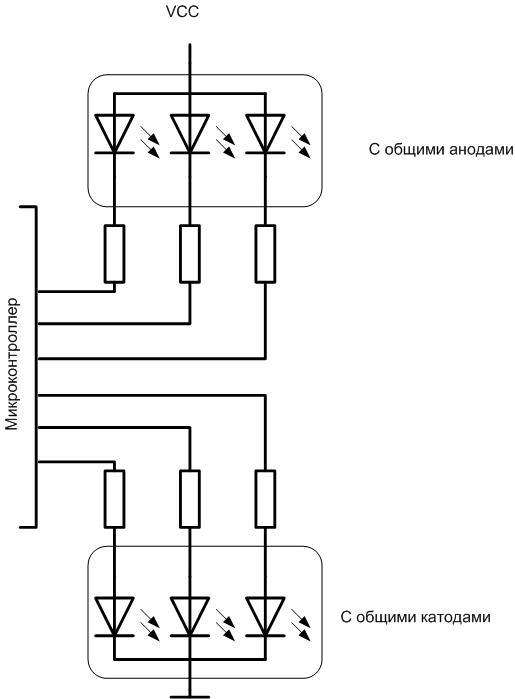
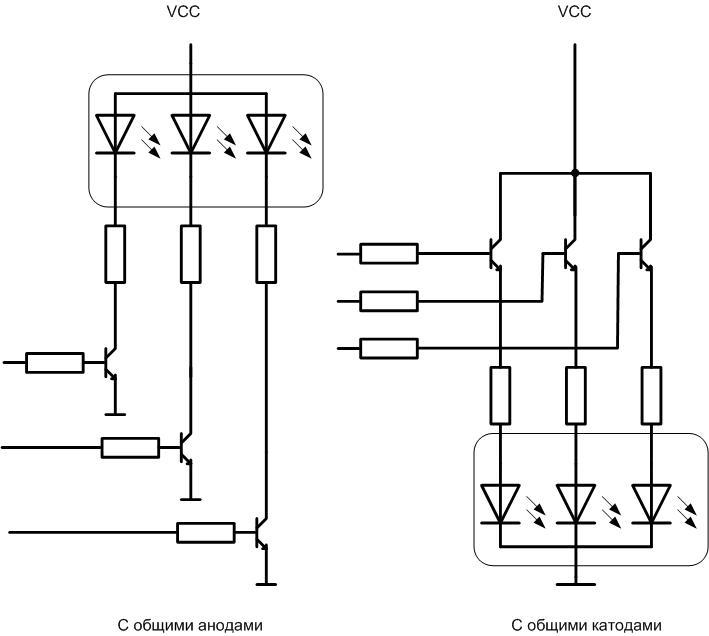
Elements with common cathodes are controlled by the output of a logical unit, with common anodes - a logical zero. It is not difficult to change the polarity of the control signal programmatically. LED with separate outputs can be connect and manage in any way.
If the outputs of the microcontroller are not designed for the rated current of the LED, the LED must be connected through transistor switches.
In these circuits, both types of LEDs are lit by applying a positive level to the key inputs.
It was mentioned that the brightness of the glow is controlled by changing the current through the light emitting element. The digital outputs of the microcontroller cannot directly control the current, because they have two states - high (corresponding to the supply voltage) and low (corresponding to zero voltage). There are no intermediate positions, so other ways are used to adjust the current. For example, the method of pulse-width modulation (PWM) of the control signal. Its essence lies in the fact that not a constant voltage is applied to the LED, but pulses of a certain frequency. The microcontroller, in accordance with the program, changes the ratio of the pulse and pause. This changes the average voltage and the average current through the LED at a constant voltage amplitude.
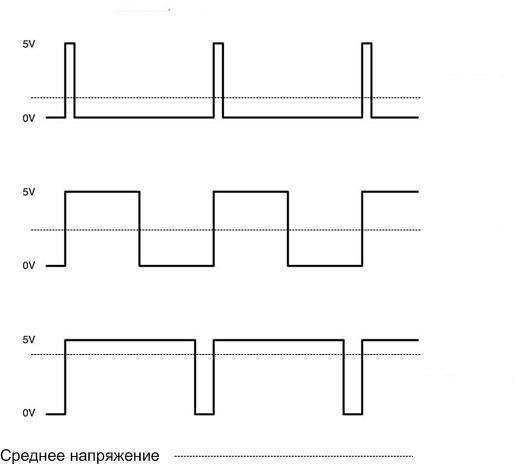
There are specialized controllers designed specifically to control the glow of three-color LEDs. They are sold in the form of a finished device. They also use the PWM method.

Pinout
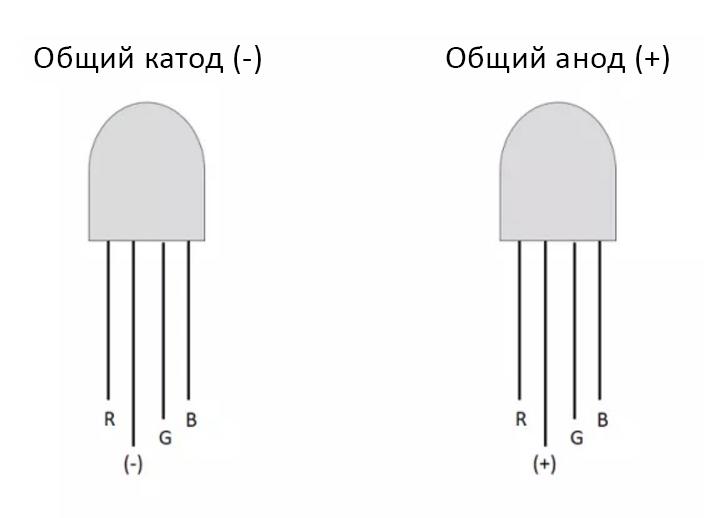
If there is a new, non-soldered LED, then the pinout can be determined visually. For any type of connection (common anode or common cathode), the lead connected to all three elements has the longest length.If you turn the case so that the long leg is on the left side, then to the left of it there will be a “red” output, and to the right side - first “green”, then “blue”. If the LED was already in use, its outputs could be shortened arbitrarily, and you will have to resort to other methods to determine the pinout:
- You can define a common wire with multimeter. It is necessary to turn on the device in the diode testing mode and connect the clamps of the device to the intended common leg and to any other, then change the polarity of the connection (as in the usual test of a semiconductor junction). If the expected common output is determined correctly, then (with all three serviceable elements) the tester will show infinite resistance in one direction, and finite resistance in the other (the exact value depends on the type of LED). If in both cases the display of the tester shows an open signal, then the output is selected incorrectly, and the test must be repeated with the other leg. It may turn out that the test voltage of the multimeter is enough to ignite the crystal. In this case, you can additionally verify the correctness of the pinout by the color of the glow of the p-n junction.
- Another way is to apply power to the intended common terminal and any other leg of the LED. If the common point is chosen correctly, this can be verified by the glow of the crystal.
Important! When checking with a power source, it is necessary to smoothly raise the voltage from zero and not exceed the value of 3.5-4 V. If there is no regulated source, you can connect the LED to the DC voltage output through a current-limiting resistor.
For LEDs with separate pins, the definition of the pinout is reduced to polarity clarification and the arrangement of crystals by color.This can also be done using the above methods.
It will be useful to know:
Pros and Cons of RGB LEDs
RGB-LEDs have all the advantages that semiconductor light-emitting elements have. These are low cost, high energy efficiency, long service life, etc. A distinctive advantage of three-color LEDs is the ability to obtain almost any shade of glow in a simple way and at a low price, as well as changing colors in dynamics.
The main disadvantage of RGB-LEDs is the impossibility of obtaining a pure white color by mixing three colors. This will require seven shades (an example is the rainbow - its seven colors are the result of the reverse process: the decomposition of visible light into components). This imposes restrictions on the use of three-color lamps as lighting elements. To somewhat compensate for this unpleasant feature, the RGBW principle is used when creating LED strips. For each three-color LED, one white glow element is installed (due to the phosphor). But the cost of such a lighting device increases markedly. RGBW LEDs are also available. They have four crystals installed in the case - three to obtain the original colors, the fourth - to obtain white, it emits light due to the phosphor.
Life time
The period of operation of a device of three crystals is determined by the time between failures of the most short-lived element. In this case, it is approximately the same for all three p-n junctions. Manufacturers claim the service life of RGB elements at the level of 25,000-30,000 hours. But this figure must be treated with caution.The stated lifetime is equivalent to continuous operation for 3-4 years. It is unlikely that any of the manufacturers conducted life tests (and even in various thermal and electrical modes) for such a long period. During this time, new technologies appear, tests must be started anew - and so on ad infinitum. The warranty period of operation is much more informative. And it is 10,000-15,000 hours. Everything that follows is, at best, mathematical modeling, at worst, naked marketing. The problem is that there is usually no manufacturer's warranty information for common inexpensive LEDs. But you can focus on 10,000-15,000 hours and keep in mind about the same amount. And then rely only on luck. And one more thing - the service life is very dependent on the thermal regime during operation. Therefore, the same element in different conditions will last for different times. To extend the life of the LED, one must be attentive to the problem of heat dissipation, do not neglect radiators and create conditions for natural air circulation, and in some cases resort to forced ventilation.
But even the reduced terms are several years of operation (because the LED will not work without pauses). Therefore, the appearance of three-color LEDs allows designers to widely use semiconductor devices in their ideas, and engineers to implement these ideas “in hardware”.