How to repair an energy saving light bulb
The failure of an energy-saving lamp is always an undesirable phenomenon. Such equipment can be repaired, with the exception of complex breakdowns. For a successful repair, you need to know the specifics of a particular circuit and the principle of operation of the light source.
Principle of operation
Any energy-saving lamp consists of several components:
- lighting flask with electrodes located inside;
- base for connecting the lamp to the network (can be threaded or pin);
- ballast (electromagnetic or electronic).
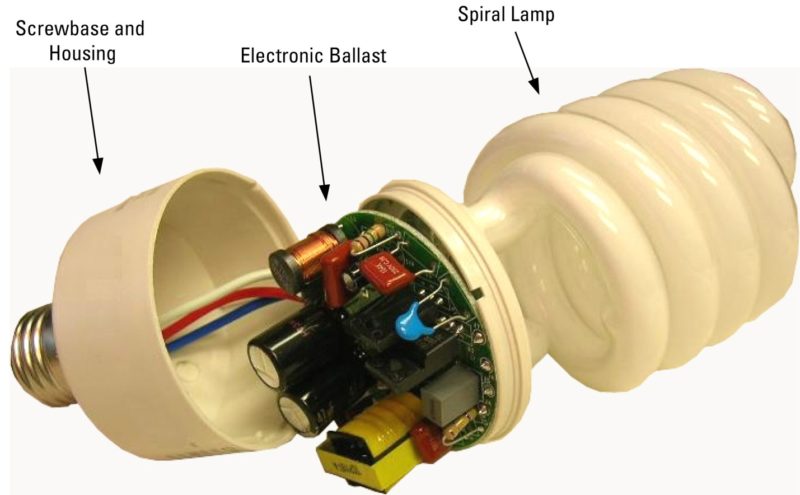
In production, the compactness of the design is important, which is provided by the built-in ballasts of the electronic type (ECG or electronic ballast).
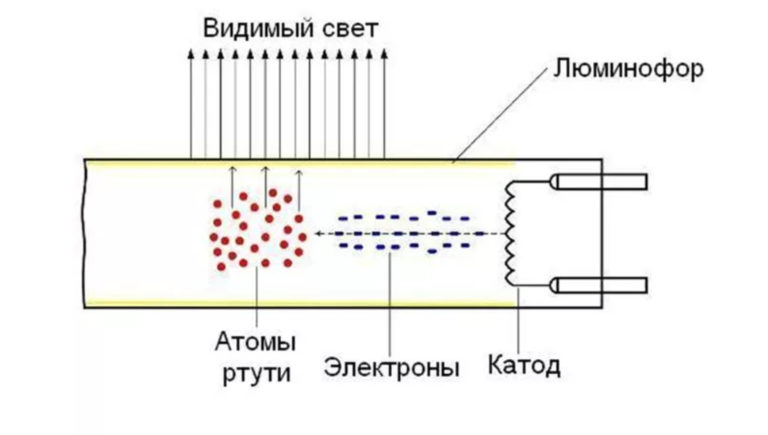
When voltage is applied to the contacts of the circuit, the electrodes inside the bulb begin to heat up. The electrons interact with an inert gas or mercury vapor inside the flask. A plasma is produced that emits ultraviolet light.
To make the glow visible to the eyes, the inside of the flask is covered with a special substance - a phosphor. This coating absorbs ultraviolet light and gives out normal white light.
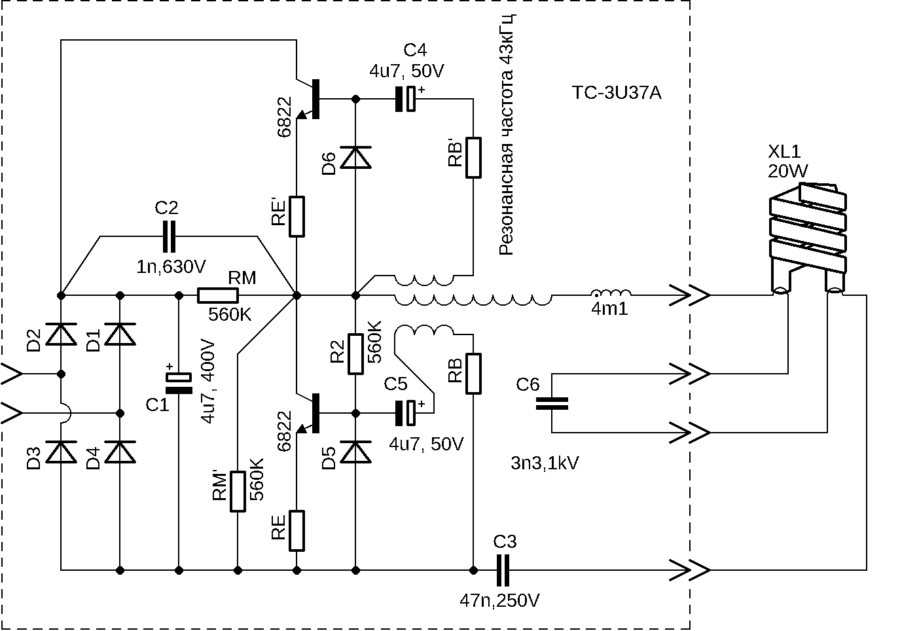
Scheme of energy-saving lamps
Under the housing of the energy-saving lamp is an electronic circuit ballast. It ensures stable operation of the device, monitors the main characteristics and prevents the elements from burning out ahead of time.
The scheme includes:
- starting capacitor, which gives a starting impulse;
- filters for smoothing fluctuations and radio frequency interference in the network;
- capacitive filter that forms the final voltage;
- a current limiting choke to protect the circuit from overload;
- transistors;
- driver for current limiting;
- a fuse that prevents overloading the circuit during power surges in the network.
Possible causes of problems
The ballast board is an important element of an energy-saving lamp. The unit is sensitive to voltage drops and may fail.
Power surges occur when there are failures in power lines, increased loads in the network, poor contacts in the socket or cartridge.
It is better not to use fluorescent lamps in closed-type fixtures with bulb down. If there is no heat output, the equipment is likely to overheat.
Causes of failure of energy-saving lamps:
- unstable voltage (too low, too high or with drops);
- jumps in network indicators;
- element overheating.
How to make repairs with your own hands
You can repair an energy-saving lamp with your own hands. You will need a set of simple tools and basic knowledge in the field of electrical engineering.
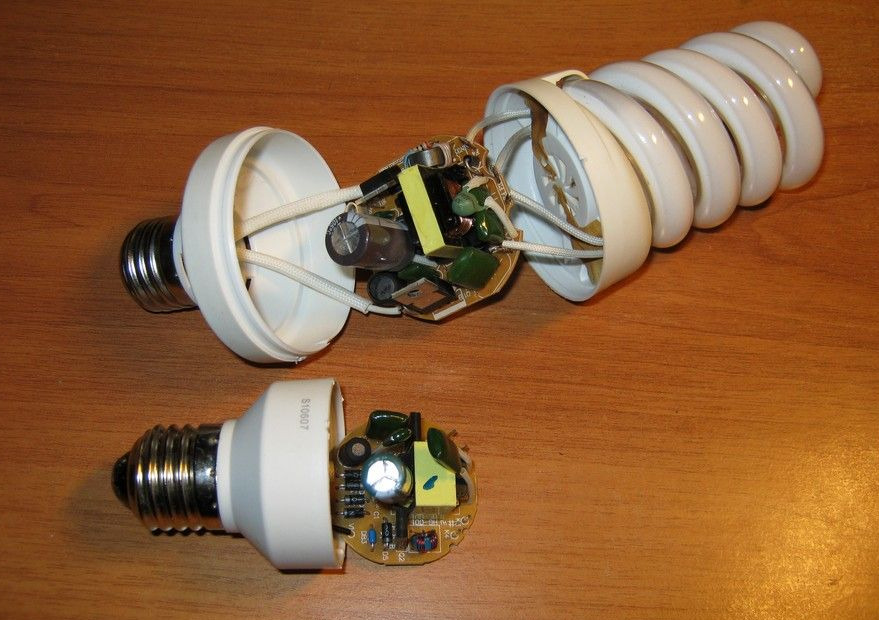
Lamp parsing
To disassemble the lamp, the base must be opened with a flat screwdriver. Unsolder the board from the base and ring the contacts.

It is advisable to prepare a wire with a plug in advance so that you can apply voltage to the board at any time.
Fault definition
After disassembly, carefully inspect the flask. If there are blackouts or burnouts on it, it is likely that the malfunction lies here. It is better to connect another flask to the electronic ballast and check performance.
If the flask is in order, the problem is most likely in the electronic ballast board. First, check the fuse with a multimeter in continuity mode, as the first frontier that protects the circuit from breakdowns.
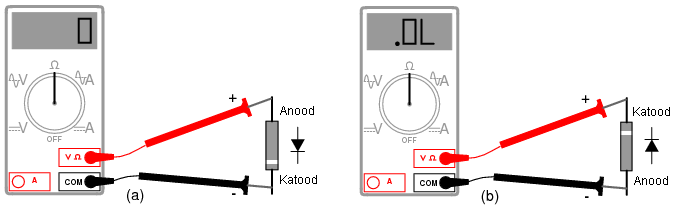
The diode bridge is checked with a multimeter. The probes are connected in series to the anodes and cathodes of the diodes. Numbers about 500 should appear on the tester's screen (when connected back, 1500). The value "1" indicates a break in the diode, and the same values in both directions indicate penetration.
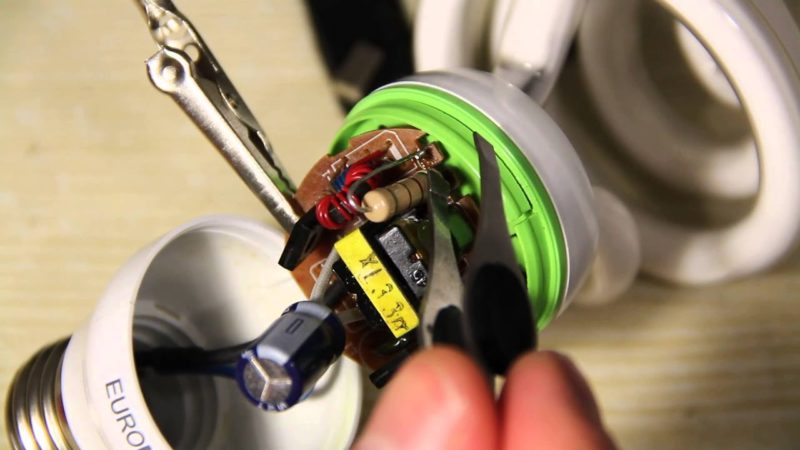
If the board has a blackened resistor in the emitter circuit, the transistor is most likely burned out. It can be called on the board without restrictions. However, the best option would be to solder with a test in diode test mode.
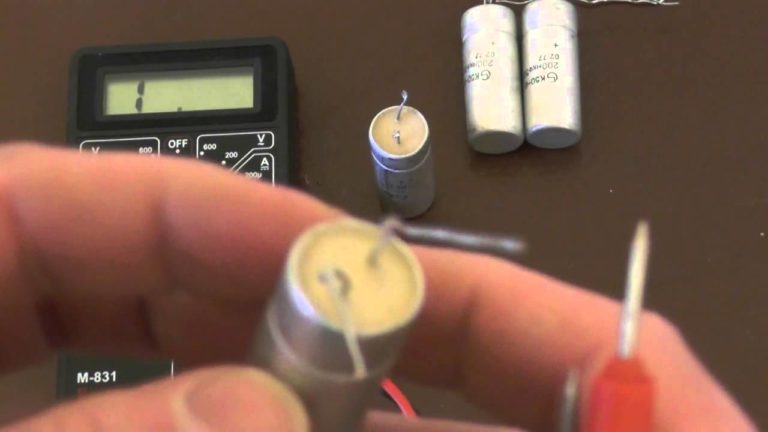
Examine the condenser. If the element is cracked or swollen, it can no longer be used. Without visible damage, you can determine the malfunction by dialing. There must be no short circuit between the plates.

You can test the capacitor by measuring the voltage. The indicator should be about 310 V at an amplitude voltage of 220 V.Significant deviations indicate a malfunction in the circuit. Replacing the capacitor will help restore the lamp to working capacity. Do not use cheap Chinese counterparts, they quickly fail.
When voltage is applied to the board, a significant current passes through the diode bridge, which can lead to burnout of the elements. To solve this problem, a current limiting resistor is used. In expensive lamps, its function is performed by a thermistor. If the element fails, the failure of the diodes and the device as a whole is a matter of time.
Lamp repair and collection
Faulty Items solder and replace with others. You can use parts from other broken energy-saving lamps, after making sure that they are in good condition.
For example, in one lamp the filament burned out, and in the other the ballast broke. Then you won’t have to solder any individual elements to the board. It is enough just to combine a serviceable bulb and electronic ballast into one device.
Use a soldering iron if you need to solder individual components of the circuit. The usual sting in this case is too large, so wind copper wire with a cross section of about 4 mm around it.

Ring diodes directly on the board will not work. Their verification is possible only after the complete removal of elements from the board. Having found a malfunction, select a new option according to the characteristics.
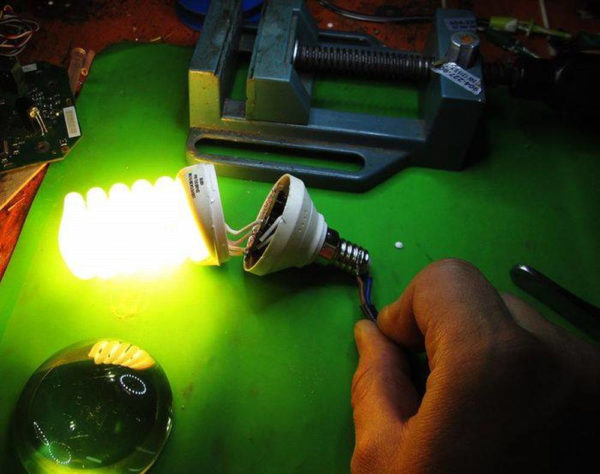
Before assembling the case, check the operation of the circuit. If the device lights up and does not flicker, you can continue the assembly.
Repairing an energy-saving lamp is a simple task and does not require significant costs. If the procedure is carried out regularly, purchase a repair kit with a set of required parts.
Safety
Since the repair of energy-saving lamps involves working with voltage, it is recommended to observe safety precautions:
- there must be an isolating transformer in the network;
- use only tools with dielectric handles;
- when repairing, a person must stand steadily on the surface;
- when applying voltage to the equipment under test, it is advisable to turn your face away;
- protective gloves will not be superfluous.

Breakdown prevention
Knowledge of faults and monitoring of key indicators will help to avoid breakdowns of energy-saving lamps.
A short circuit inside the lamp may occur due to a manufacturing defect or insufficient heat dissipation. In any case, during operation, the circuit overheats, and the insulating layer is broken. Eventually, some wires or contacts begin to come into contact with each other. It is desirable to provide all fixtures with sufficient ventilation and a well-thought-out heat dissipation system.
Related video: 6 homemade products based on an energy-saving lamp.
Often, in order to save money, manufacturers use not the highest quality components. This leads to a breakdown of the ballast. The fault will quickly manifest itself in conditions of significant voltage drops. Therefore, it is better to equip the supply network with a high-quality stabilizer.
The problem of burnout is not alien to energy-saving lamps. It cannot be corrected or prevented. You can only create suitable conditions without voltage drops, frequent on and off, with a stable ambient temperature.