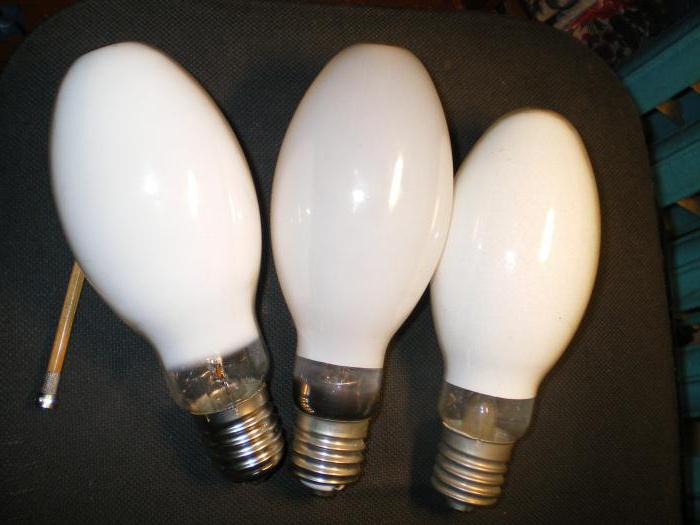
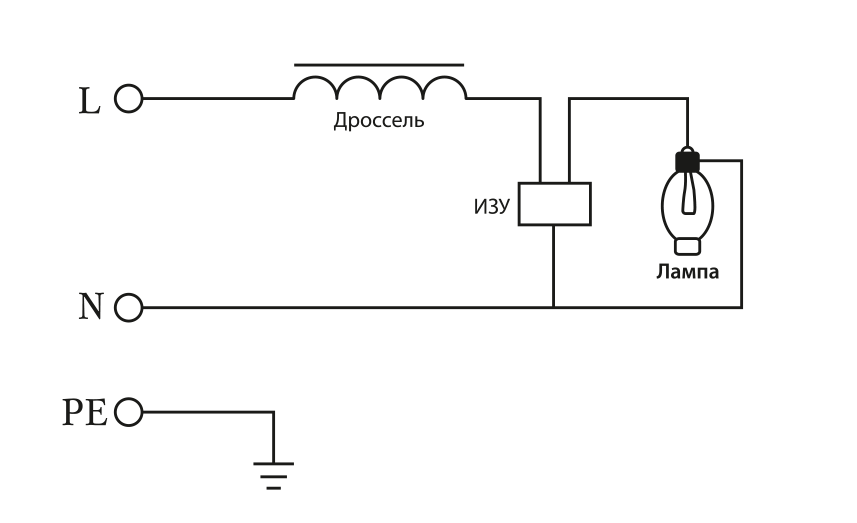
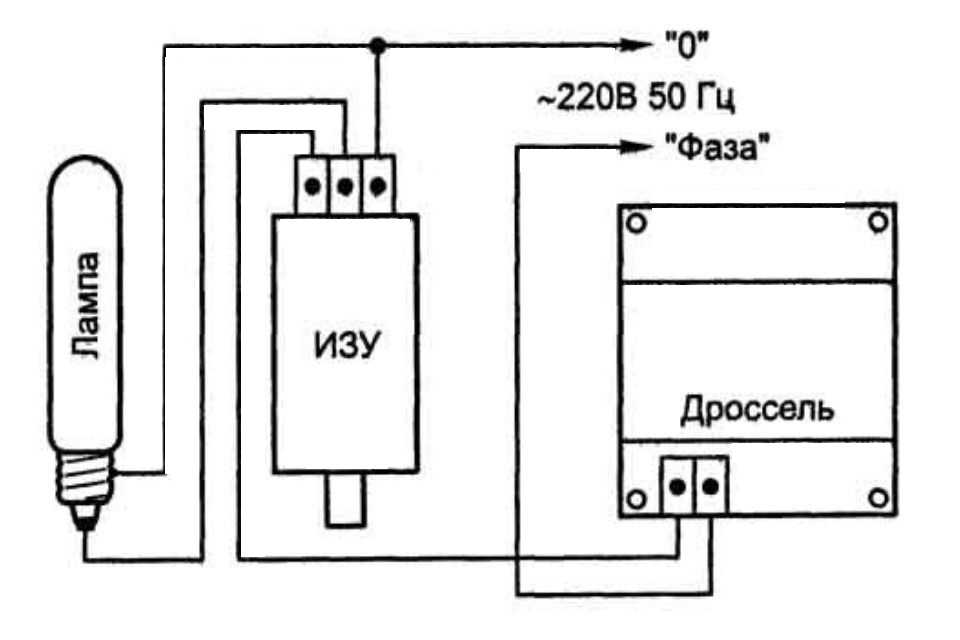
What does the abbreviation DNAT mean?
Sodium lamps - a type of energy-saving lighting elements, inside the bulb of which is sodium. The design is old and is being replaced by more technologically advanced light sources. However, it is still in demand, so it makes sense to consider it in detail.
What is a sodium lamp
A sodium lamp is understood as a lighting device with the designation DNaT and the decoding “arc sodium tubular” lamp. The element is reliable, simple and affordable. Many companies still produce them, which indicates the presence of demand.
The devices first appeared in the thirties, but they were quickly replaced by metal halide sources. Elements are used for street lighting, illumination of agricultural crops, in sports halls and underground passages.
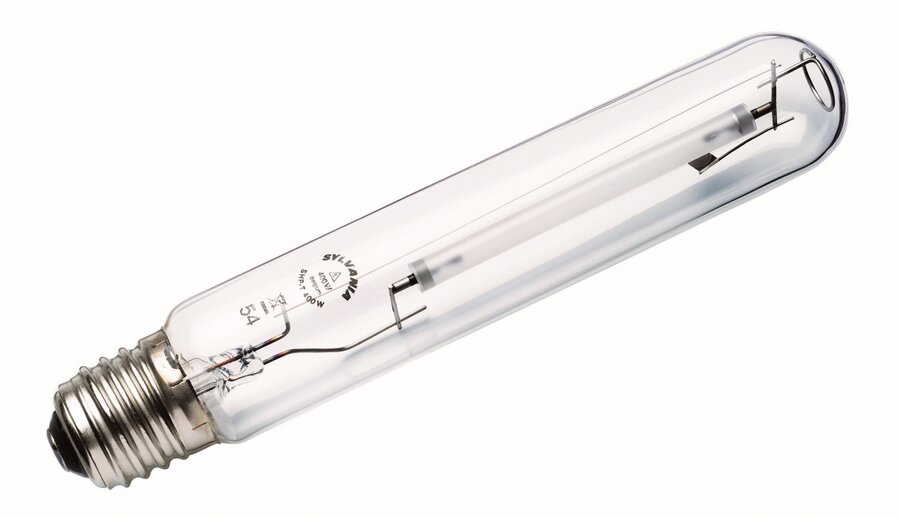

For a long time, sodium cells were installed in street lamps and track lighting systems.Devices are now being replaced with LEDs. However, a large number of designers prefer sodium sources due to their availability, long life, high power and light output.
HPS are often installed at enterprises together with metal halide lamps. Sodium lighting gives warmer hues and is more comfortable to work with.
Varieties
All sodium lamps are divided into high and low pressure elements. The main difference is in the level of pressure in the flask and the difference with the atmospheric indicator. This determines the specifics of the equipment operation and application in specific situations.
High pressure
There are three types of high pressure elements:
- HPS is the most common high pressure sodium arc lamp found in street lamps.
- DNaZ is a type of DNaT, which has a mirror coating on the inner wall of the flask. The element is characterized by lower power, but increased light output.
- DRI (DRIZ) - a device with radiating additives. May have a mirror layer on the flask. Relatively good color reproduction, but some colors look dull.

Low
sodium low pressure lamps from the very beginning were not popular with users and are not used now. Even increased energy efficiency did not become a reason to use it. The reason is poor color reproduction, which makes it difficult to identify the color, and sometimes the shape of the object.
At the same time, they are reliable, consume little energy, give excellent light. Suitable in rare cases exclusively for street lighting.
Specifications
The main ones include luminous flux, light output and operating time.There is a direct relationship between the power of the element and the resource - high power models work longer.
Below are the technical characteristics of popular HPS sources with a power of 150, 250 and 400 W. All of them are connected to the luminaire using an E40 socket with a voltage of 120 V.
DNAT 150
Technical characteristics of the lamp DNAT 150
| Power, W | Flux, lm | Light output, lm/W | Length, mm | Diameter, mm | Resource, h |
| 150 | 14 500 | 100 | 211 | 48 | 6 000 |
DNAT 250
Technical characteristics of the lamp DNAT 250
| Power, W | Flux, lm | Light output, lm/W | Length, mm | Diameter, mm | Resource, h |
| 250 | 25 000 | 100 | 250 | 48 | 10 000 |
DNAT 400
Technical characteristics of the lamp DNAT 400
| Power, W | Flux, lm | Light output, lm/W | Length, mm | Diameter, mm | Resource, h |
| 400 | 47 000 | 125 | 278 | 48 | 15 000 |
Design features
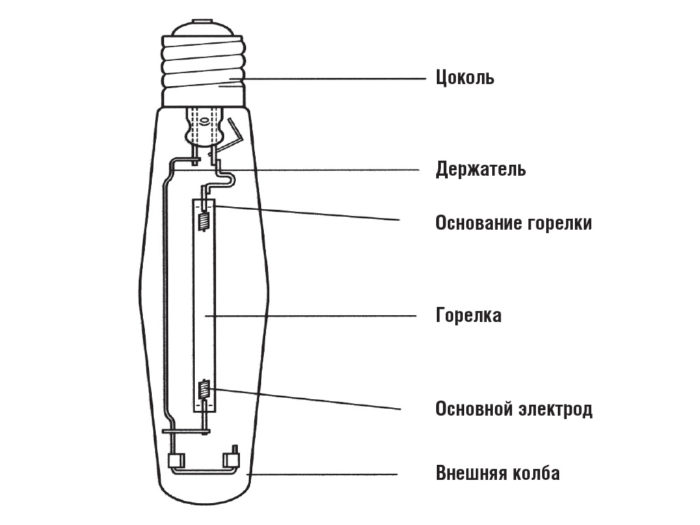
All sodium lamps are a high-strength aluminum oxide bulb connected to two electrodes. The material of the element withstands high temperatures and is resistant to sodium vapor. The flask is filled with a mixture of inert gases, mercury, sodium and xenon. The presence of argon in the gas mixture facilitates the formation of a charge, while mercury and xenon serve to improve light output.
The design looks like a flask in a flask. The burner is installed in a smaller flask, a vacuum is created in it. Connects to the network through the plinth. The outer element performs the function of a thermos, protecting the internal parts from the negative effects of low ambient temperatures and reducing heat loss.
Burner
The burner is the most important element of any HPS lamp. It is a thin glass cylinder, the most resistant to temperature extremes and chemical attack. Electrodes are inserted into the flask on both sides.
During the production of the burner, special attention is paid to its complete vacuumization. The base during operation of the equipment heats up to 1300 degrees and the ingress of even a small amount of oxygen into this area can lead to an explosion.
Video: Lamp DNAT 250 with a depressurized flask.
The burner is made of polycrystalline aluminum oxide (policor). The material has a high density, resistance to sodium vapor and transmits about 90% of all visible radiation. The electrodes are made from molybdenum. Increasing the power of the element requires increasing the size of the burner.
The vacuum in the flask is difficult to maintain, because with thermal expansion, microscopic gaps inevitably appear through which air passes. To prevent this, spacers are used.
plinth
Through the base, the lamp is connected to the mains. The most commonly used Edison screw connection marked E. For HPS with a power of 70 and 100 W, E27 socles are used, for 150, 250 and 400 W - E40. The number next to the letter indicates the connection diameter.
For a long time, sodium lamps were equipped only with screw bases, but not so long ago a new Double Ended connection appeared, providing contacts on both sides of a cylindrical bulb.

Operating principle
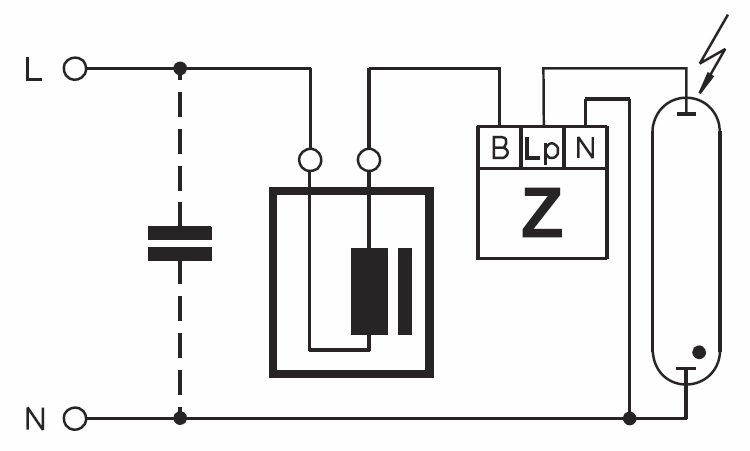
Inside the bulb of a sodium lamp, an arc discharge must be maintained. For generation, a pulse igniter (IZU) is used. During switching on, the pulse can reach a power of 2-5 kW.
Under the action of voltage, a breakdown occurs with the formation of a discharge. It takes about ten minutes to warm up the burner and bring the device to rated power. At this time, the brightness increases and normalizes.
In modern elements, you can find a built-in choke, which limits the strength of the arc current and guarantees a stable supply of energy without ripples and other undesirable moments.
Applications
Sodium lamps are used when economic considerations are more important than color rendering. They are not suitable for residential premises, public buildings and production halls.. In addition to poor color reproduction, the lamp is dangerous if it malfunctions.
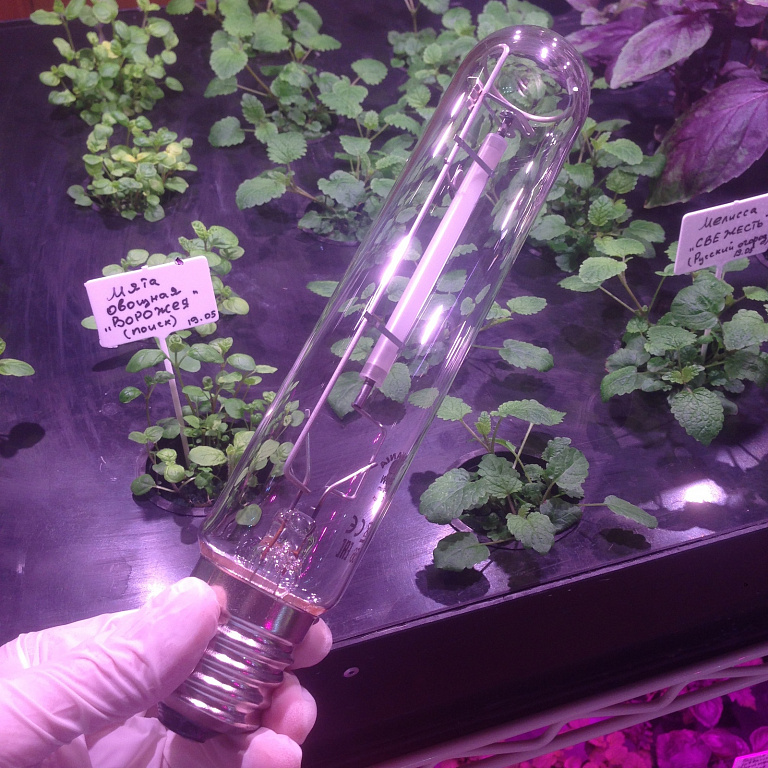

DNAT is used to organize street or greenhouse lighting, illumination of architectural monuments and buildings. They are especially common in large cities. They can be recognized by their yellowish-golden hue. The most common elements with a power of 250 and 400 watts.
Relatively recently, low-power sodium lamps with a color rendering index of 80 appeared on the market. This indicator is much higher than that of other similar models. Therefore, such lamps are effective for light decoration in public places.
Sodium light sources are used in the last stages of seedling growth in greenhouseswhere shades of blue are often present. Radiation of a significant part of the ultraviolet spectrum promotes plant growth. It is important to handle the elements with care, because. the destruction of the flask can ruin the entire crop and spoil the soil.
Designers often use sodium elements to simulate fire or the light of the sun.
Wiring diagrams
Depending on the IZU, the schemes differ. IZU is two-pin and three-pin. Below are diagrams for both cases.
In sodium lamp circuits, the inductor is always connected in series, while the igniter is connected in parallel.
Power reactivity during starting requires the inclusion of a capacitor in the circuit to reduce noise and inrush current. Typically, an element with a capacity of 18-40 microfarads is used. The capacitor is connected in parallel with the power supply. The capacitor stabilizes the voltage and slows down the degradation of the electrodes.
Precautionary measures
When using gas discharge sodium lamps, it is important to remember:
- It is unacceptable to turn off the power supply of the slice element after it has been turned on. You need to wait at least 1-2 minutes. Neglecting the recommendation can lead to a complete launch failure.
- The room with the lighting element must have a ventilation system. This is due to the increased heat transfer of the device and the presence of harmful substances in it.
- Do not touch the lamp and reflector during operation with bare hands, this is guaranteed to cause a serious burn.
- When installing the flask, it is advisable to use gloves. A fatty coating when heated can lead to an explosion of the flask. Water contact with open elements is prohibited.
- Used together with a light bulb, the ballast can be heated to temperatures of about 150 degrees. It is recommended to stow it under a fireproof casing to protect it from moisture and debris.
- Do not handle conductive parts with bare hands or allow them to get wet. It is also recommended to periodically check the wiring for damage, burns or short circuits.The wires in this case must be special, designed to work with extremely high voltages.
Disposal
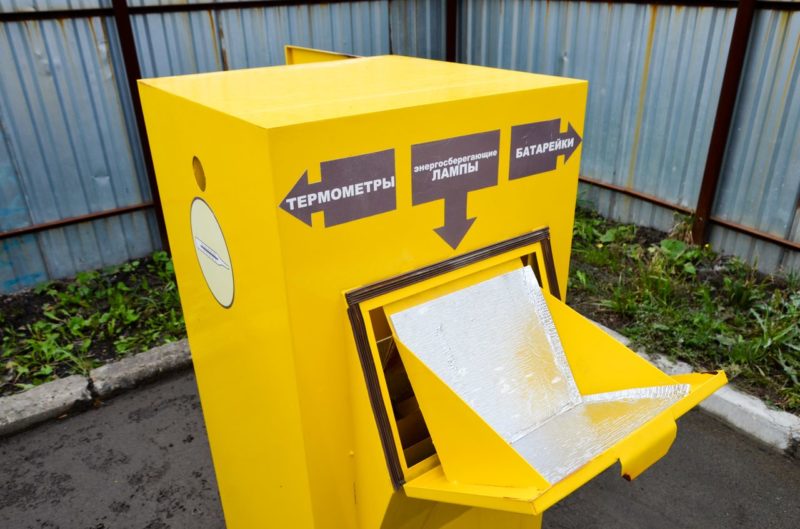

Sodium is a volatile substance that ignites easily on contact with air. In addition, the elements contain mercury - a dangerous radioactive element that can cause severe poisoning. For this reason, simply throwing away sodium light sources is unacceptable. They must be disposed of as potentially hazardous waste along with other energy-saving lamps.
Tanks are provided for disposal in large cities. If this is not possible, contact your nearest lighting workshop, manufacturing facility or call the hazardous waste collection service.
Advantages and disadvantages
The sodium lamp has both advantages and disadvantages. Given them, you will avoid unpleasant surprises.
Advantages:
- High light output compared to other lighting fixtures. For NLVD, the indicator can reach 150 lm / W, and for NLND even 200 lm / W.
- Most of the presented models are able to work for a very long time, and the maximum resource is 28,000 hours.
- During the operation period, the efficiency parameters remain at the same level.
- The devices emit light that is very comfortable for the eyes.
- Sodium lamps are able to function stably at temperatures from -60 °C to +40 °C.
There were some shortcomings, which include the following:
- It may take about 10 minutes from the moment of starting until reaching the nominal power.
- Many elements inside the flask contain harmful mercury.
- Explosion hazard associated with the likelihood of sodium contact with air and rapid ignition.
- Sometimes it is difficult to connect ballasts.
- During operation, significant power losses (up to 60%) are observed.
- Color reproduction is low.
- When connected to a 50 Hz network, significant ripples are observed.
- It takes a lot of voltage to ignite.
The disadvantages are significant, however, for the organization of high-power street lighting, sodium sources seem to be a convenient option.