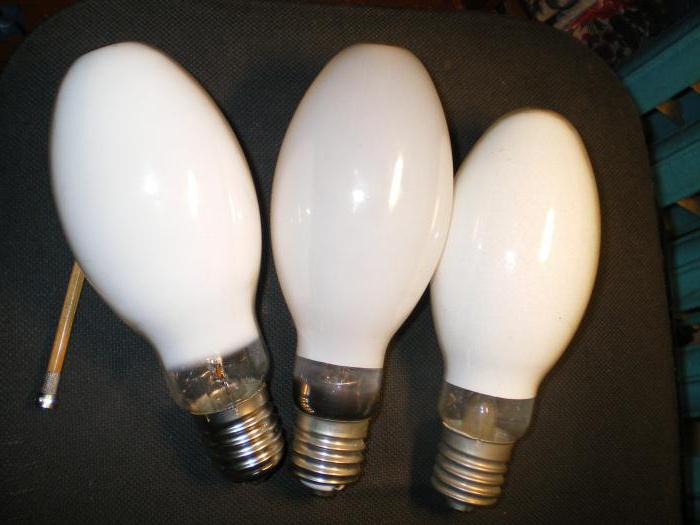
Description of the DRL lamp
DRL lighting sources are very reliable and efficient and are widely used in a variety of fields. However, for proper operation, it makes sense to familiarize yourself with the devices in more detail.
What is a DRL lamp
The abbreviation DRL stands for "arc mercury lamp". Sometimes there is an abbreviation RL. In some documents, the letter "L" means "phosphor", since it is he who is the main source of light in the device. The element belongs to the category of high-pressure discharge lamps.
The marking of a specific model contains a number indicating the power of the equipment.

Pros and cons
DRL sources have long been used to illuminate streets and premises. During this time, users managed to highlight the advantages and disadvantages that determine the choice:
Advantages:
- good light output;
- high power;
- relatively small body size;
- low price compared to LED;
- economical energy consumption;
- most of the products are capable of working for 12,000 hours (the indicator depends on the quality of the components used).
There are also disadvantages that are important to consider:
- inside the flasks there are harmful mercury vapors that can cause poisoning in case of leakage;
- some time passes from switching on to reaching the rated power;
- a preheated lamp cannot be turned on until it cools down (about 15 minutes);
- sensitive to power surges (a deviation of 15% will cause a change in brightness by 30%);
- equipment does not work well at low temperatures;
- during operation, a pulsation of light is observed;
- low color rendering;
- elements are very hot;
- in the circuit, you need to use specialized heat-resistant components (wires, cartridges, etc.);
- the arc element requires ballasts;
- sometimes the included element makes an unpleasant sound;
- in the room where the lamps are working, it is necessary to have ventilation to weather the ozone;
- over time, the phosphor loses its properties, which leads to a weakening of the light flux and a change in the spectrum.
Most of the disadvantages are inherent only in cheap DRLs from dubious manufacturers and are insignificant when a powerful source of illumination is needed.
Lamp design
Initially, the designs used burners with two electrodes, requiring the installation of an additional module for generating pulses when turned on. The voltage they created was much higher than the operating voltage of the lamp.
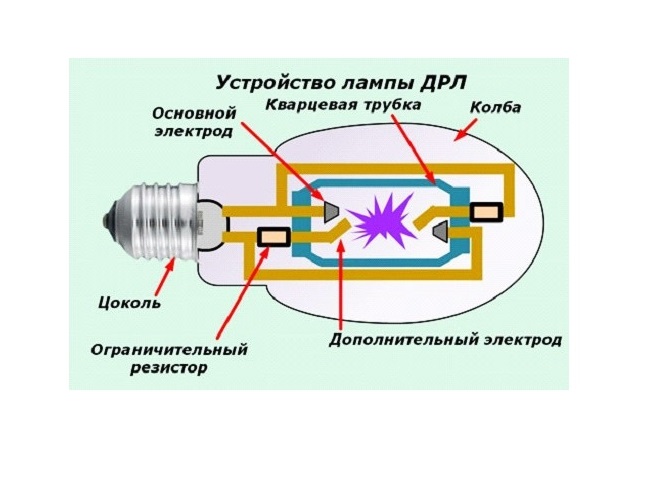
Later, two-electrode cells were replaced by units with four electrodes. It became possible to abandon external equipment that generates impulses for ignition.
The DRL lamp consists of the following components:
- main electrode;
- ignition electrode;
- electrode leads from the burner;
- a resistor that provides the desired circuit resistance;
- inert gas;
- mercury vapor.
The main flask is made of durable glass, resistant to high temperatures. The air is pumped out and replaced with an inert gas. The main function of the inert gas is to prevent heat exchange between the heater and the flask. But even in this case, the body of the equipment during operation can heat up to 120 degrees Celsius.
A base is provided for connecting the lamp to the network. It allows you to fix the equipment in the cartridge and provides the most tight contact.
The inside of the flask is covered with a phosphor, which converts invisible ultraviolet radiation into a visible glow. Under the influence of UV rays, the phosphor heats up and begins to emit light. The shade of light depends on the composition of the coating.
The main luminous element inside the bulb is an electric arc between the electrodes.
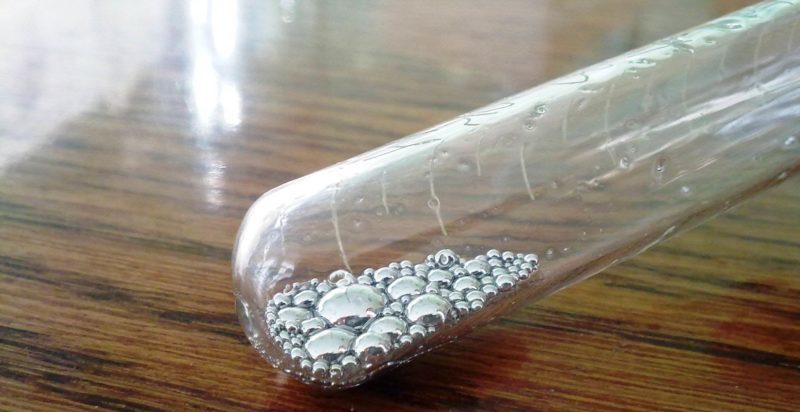

Mercury acts as a stabilizer for the movement of electrons and in a cold device it can look like small balls. With a slight heating, mercury turns into steam and interacts with the internal structural elements.
The burner itself looks like a small tube of glass or ceramic. The main requirements for the material: the preservation of properties at high temperatures and the ability to transmit ultraviolet rays.
Resistors in the circuit limit the current and prevent other elements from failing ahead of time.
Principle of operation
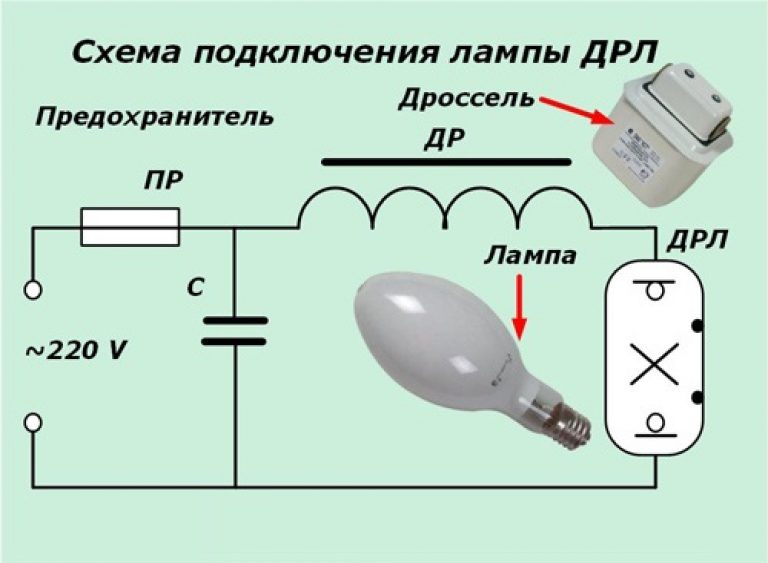
The principle of operation of the DRL provides for the presence of a light source, a capacitor, a choke and a fuse.
When voltage is applied to the electrodes, gas ionization occurs in the free region. A breakdown and an arc discharge occur between the electrodes. The glow of the discharge can be bluish or purple.
The phosphor is selected red. When the spectra are mixed, the output is pure white light. The hue can change when the voltage applied to the contacts changes.
Thematic video: Device, principle of operation and features of operation of DRL lamps.
Getting to the desired brightness in the DRL takes about 8 minutes. This is due to the gradual melting and evaporation of mercury balls. It is mercury vapor that ensures the stability of the processes inside the burner and improves the glow of the device. The maximum brightness appears at the moment of complete evaporation of mercury.
It is worth noting that the ambient temperature and the initial state of the lamp affect the rate at which it reaches its rated power.
The throttle in the circuit is a primitive ballast. With its help, the system controls the strength of the current passing through the electrodes of the structure. If you try to bypass the choke to connect the lamp directly to the network, it will fail very quickly.
Now most of the electronic equipment manufacturers are moving away from the choke as an outdated solution. Arc stabilization is carried out by electronic devices that provide the desired performance even with significant voltage drops in the network.
Specifications
The main technical characteristic of sources of this type is power. It is she who is indicated in the marking of the device next to the abbreviation DRL. The remaining parameters should be considered separately. They are indicated on the box or in the equipment passport.

These include:
- Luminous flux DRL. Determines the effectiveness of the device when illuminating a specific area.
- Resource. The service life of the equipment, subject to the basic recommendations.
- Plinth. Designation of how the model is embedded in lighting equipment.
- Dimensions. A less important characteristic that determines the use of the model in specific fixtures.
DRL 250
Technical characteristics of lamps DRL 250
| Power, W | Luminous flux, Lm | Resource, h | Dimensions (length × diameter), mm | plinth |
| 250 | 13 000 | 12 000 | 228 × 91 | E40 |
DRL 400
Technical characteristics of DRL 400 lamps
| Power, W | Luminous flux, Lm | Resource, h | Dimensions (length × diameter), mm | plinth |
| 400 | 24000 | 15000 | 292 × 122 | E40 |
Scope of application

All DRL sources are used to illuminate large areas. Most often they are built into street lights, road lighting systems and gas stations. Often they organize lighting of large warehouses and other premises where the color rendering parameter is not fundamental, as well as in exhibition centers. The high power of the devices is very handy.
They are not used in residential buildings and apartments, because. poor color reproduction and a long turn on make this solution ineffective.
Life time
The service life of DRL lamps directly depends on the power. The most common DRL 250 is able to work for about 12,000 hours without any problems. It is important to remember that the following factors can reduce the resource:
- frequent switching on and off;
- voltage drops;
- continuous use at low ambient temperatures.
All this leads to accelerated degradation of the electrodes and, as a result, rapid failure.
Disposal
The presence of mercury in DRLs refers them to the first hazard class. In a number of countries, such devices are prohibited for use. However, compliance with the rules of operation and disposal minimizes all risks to humans and the environment.
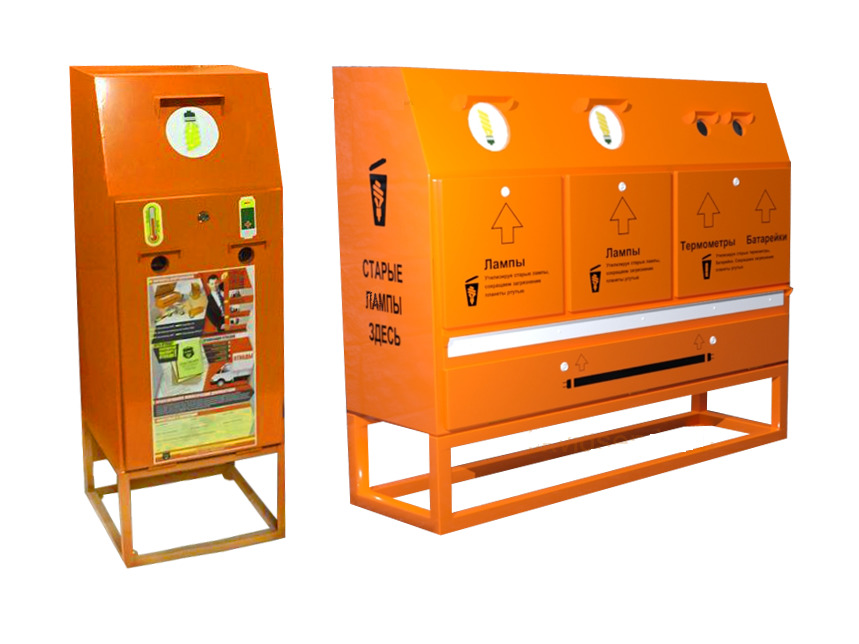

It is forbidden to throw away such light sources together with ordinary garbage. Mercury released into the environment can significantly harm the environment.
Disposal of DRL is carried out by the same structures that work with other energy-saving lamps. The company must have a state-issued license allowing such work to be carried out.
In large cities, you can find special tanks in which spent elements are placed. You can also contact utilities, lighting manufacturers or repairers, or hazardous waste disposal companies.
