Which wire to choose for wiring in the apartment
The choice of conductor products for arranging internal or external lighting is a responsible decision. An error can lead to serious consequences - the inoperability of the system, overheating of the wiring, and even fire. The right choice can only be made consciously, for this you need to familiarize yourself with the main selection criteria.
cable or wire
The first step is to deal with the question posed in the title. At the household level, these concepts are approximately equivalent. Those who are close to electrical engineering and have a superficial knowledge of regulatory documents often argue that a wire contains one conductive core, and a cable contains two or more (referring to GOST 15845-80).In fact, there are cables with one conductor (for example, PvPu 1x95), and there is a wire consisting of several conductive elements. So, a self-supporting insulated wire (SIP) consists of three conductors in separate insulation, twisted around a carrier cable.
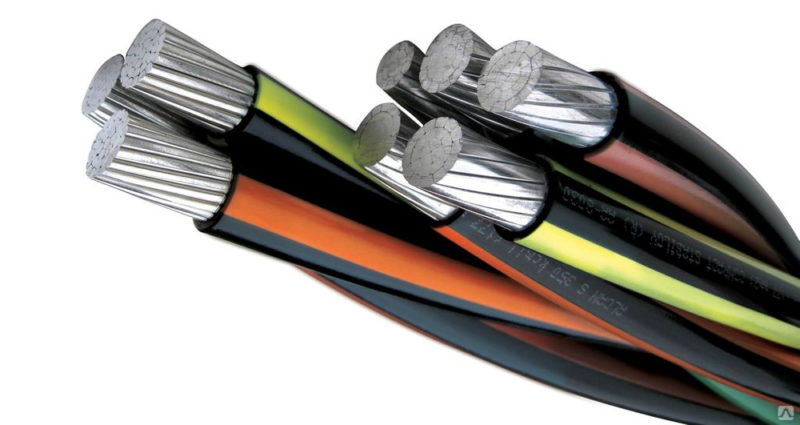

Really difference between cable and sheathed wire. The wire has a light single-layer insulation. If the cable consists of several wires with independent insulation, then they are enclosed in one common sheath. This shell can have a reinforced structure, up to an armored one. This allows you to lay conductor products in any way, including underground (wires are not laid underground without additional protection). The same applies to single-core cables. Thus, the APvPug cable has a stranded conductor, XLPE insulation and a multilayer additional sheath, including an armor layer.

Applications in lighting systems
To organize lighting, you can use both wires and cables, depending on the conditions:
- it is convenient to use cables for wiring in rooms - three conductors (phase, zero, ground) are laid simultaneously;
- wires can be installed in switchboards or wiring where it is difficult to lay the cable;
- on the street, for the most part, cables are used - because of the increased mechanical strength, the security of the conductive cores, and also because of the mentioned convenience;
- when laying in a suspended way (overhead lines, etc.), it is convenient to use SIP - no additional cable is required.
In difficult cases, you need to look at the situation, but it is always better to focus on the cable - for reasons of reliability.
Selection of conductor products
Wiring in the house or in the country is not done for one year. Before purchasing a cable (or wire), you need to pay attention to some important points to avoid problems in the future.
Material and design
For laying in an apartment, it is necessary to use a copper wire - this is the requirement of the PUE. There is a permissive use of aluminum conductors with an aluminum core, and its cross section must be higher than that of a copper wire in the same situation.
| Line | The smallest section of veins, sq. mm. | |
| copper | aluminum | |
| Group networks | 1,5 | 2,5 |
| From storey to apartment panels | 2,5 | 4,0 |
| Distribution network (risers) for supplying apartments | 4,0 | 6,0 |
It must be understood that this decision was made in favor of the manufacturer, and not because of technical advantages. Aluminum is ductile, so the clamp contacts will periodically loosen, resulting in an increase in contact resistance. The surface of this metal is constantly covered with an oxide film, which also does not contribute to good contact. And the eternal problem of aluminum wiring is the fragility of the cores.
It should also be borne in mind that an increased cross section will require increased sizes of terminals and lugs. Therefore, if the wiring is done "for oneself", it is necessary to use a cable with copper conductors, although this is more expensive.

For the installation of 220 volt household networks, it is necessary to choose a cable from three conductors:
- phase;
- zero;
- grounding.
This choice will allow you to lay the conductor products once. If there is no PE conductor in the lighting system, a line with two wires is sufficient.
Conductor cross section
The cross-section of the wire for consumers and lighting is selected on the basis of the paragraphs of the Rules for the Installation of Electrical Installations, which establish the minimum cross-sections of the conductors. The actual value is selected according to the actual load according to table 1.3.4 of the PUE. When purchasing products using a caliper or micrometer, you can control what section the cable actually has. With a large deviation to the smaller side, it is better to refuse the purchase.
Important! For calculations, you need to know the cross section of the conductor S, not its diameter D, therefore, its measured size must be converted into a cross section according to the formula S=π*(D/2)2 or use a table.
| Measured diameter, mm | 1,4 | 1,8 | 2,25 | 2,75 |
| Corresponding actual section, sq. mm | 1,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 |
Strictly speaking, during production, it is not the diameter that is normalized, but the resistance of one meter of the core, and this parameter also depends on the material of the conductor. Therefore, a slight downward deviation is allowed. Conversely, matching the diameter may mean nothing due to the use of poor quality copper. Therefore, the best way to determine the quality of a cable for lighting in a house or apartment is view the certificate. It must contain GOSTs (or TUs with reference to GOSTs) for the core material. The same applies to other cable parameters - insulation quality, etc.
Core color coding
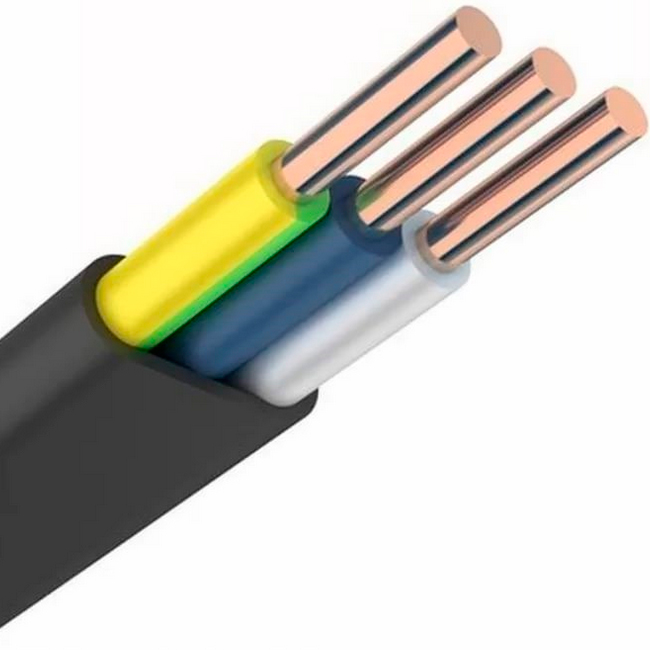
Each sheathed conductor is individually insulated. It may have the same color for all three wires. And it's better when each wire has its own color. The use of the following colors for a three-wire cable has become the standard:
- red or brown (for phase wire);
- blue (for zero);
- green or yellow-green - for grounding.
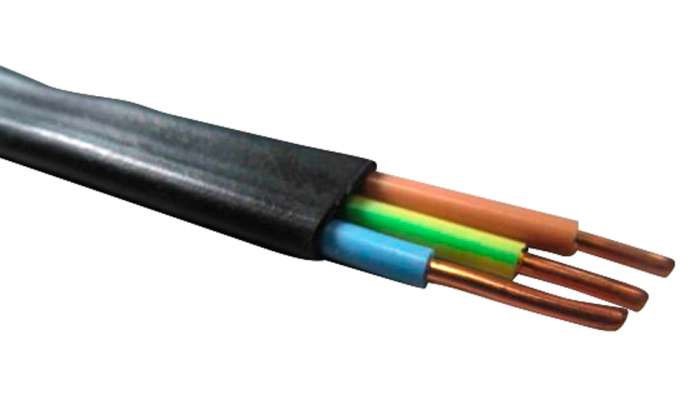
If the colors do not match the standard or all the wires are the same color, this will not lead to the inoperability of the circuit. But such a wire for lighting will complicate installation and - in the future - repair.
Insulation and sheath thickness
The insulation of each core and the common sheath is made of various dielectric materials. Standards set the thickness of the individual coating. For products with a cross section of 1.5 and 2.5 sq. mm. it should be at least 0.6 mm. The thickness of the overall sheath should be from 1.8 mm for stranded products and from 1.5 mm for single-core products. Insulation with these mechanical parameters will provide strength when cutting and cutting, but will not create problems when laying, while maintaining flexibility. In fact, the quality of the insulation is equally important. It is better to check it with a megger for a voltage of 1000 volts. It should show a resistance of at least 1 MΩ.
Important! It is necessary to measure the insulation resistance after cutting, laying and cutting the cable, but before connecting switching devices and consumers.
Cable marking
The letter designation of the cable can give a lot of information. So, if the first letter in the marking - BUT, then this product has aluminum strands. If any other letter is copper. letter To in the name it has a control cable (with copper conductors), for measurement and signaling circuits, and if at the beginning of the marking P - it's a wire. Next (or first in the absence of A, P or To) the letter means the insulation material of the common sheath:
- R - rubber;
- AT - polyvinyl chloride;
- To - capron
- P - polyethylene;
- other materials.
The next letter shows what the individual core insulation is made of. It is selected from the same list as the previous one.Further there may be letters indicating other properties of the conductor product:
- G – flexible;
- ng - non-combustible;
- Ls – Low Smoke, with low smoke emission when heated;
- B - the presence of armor;
- P - flat;
- other designations.
The letters are followed by numbers indicating the number of cores and their cross section. Yes, marking AVVG 3x6.0 has an aluminum cable with insulation of each core from PVC, the overall sheath is made of the same material, flexible with three cores with a cross section of 6 sq. mm. each. And the combination VVG 3x6.0 the same product is marked, only with copper conductors. If the cable is marked KVVGngLs 3x1.5, then it is a control cable with core insulation and an overall sheath of non-combustible PVC, which forms a small amount of smoke and has three cores of 1.5 sq. mm.
Package
Conductor products enter retail and small wholesale trade in bays. The total cable length is several hundred meters. Such an amount is in most cases unnecessary, but sellers usually cut off the required length, starting from one meter.
Visual inspection
When buying any amount of cable products, it will not be superfluous to inspect the purchased product, despite the presence of a certificate and assurances from the seller. It is necessary to pay attention to the integrity of the insulation, the absence of cracks and abrasions, the absence of corrosion on the cut of the cores. You also need to know that under the sharp bends of the cable, conductor fractures or cracks in the insulation can be hidden. If all or part of the defects are present, it is better to refuse the purchase.
PUNP is a bad option
The cable is still on sale. PUNP at an attractive price. It should not be used in any case, especially in a wooden house.The fact is that the technical conditions under which this cable is produced (although it is a wire according to the marking) allow a significant reduction in the cross section of the conductive cores (against the declared one), and also allow a decrease in the thickness of the insulation. Therefore, this wire (?) is prone to overheating and even fire, which is confirmed by statistics.

Also not recommended for use apartments conductor products with stranded conductors. The reason is the same - increased fire hazard due to poor resistance to heat.
Choice of section and brand of cable
The most popular cable for household wiring is VVG of the appropriate section. This is a good domestic product, it has basic and additional PVC insulation and is available in several versions:
- VVG - common product
- VVGng – insulation does not support combustion;
- VVGng-Ls – self-extinguishing jacket with low smoke emission;
- VVGngFR-Ls - with additional fire protection.
The VVGng cable corresponds to the foreign analogue NYM.
Important! On sale there are products with marking NUM. This "accidental" typo indicates that the cable is not original and its parameters are on the manufacturer's conscience.
Sections must be selected for the existing and expected load. But there are situations when consumers are not completely known (for example, during the construction of a new house or during the overhaul of an apartment). In such cases, one can be guided by the values of the cross sections developed by experience.
For input
During the construction of an apartment building, the power consumed by one apartment is laid down during the design. Under this value, the vertical wiring of the entrance (“risers”) is also calculated.For normal energy consumption, the input to the apartment is done cable with a cross section of cores from 6 to 10 sq. mm. This is enough for any load within reason. It is not worth exceeding the power limit, which limits the cross section at the input to 10 sq. mm. This can lead to an overload of the common house wiring.
For lighting
For residential lighting network in 99+ percent of cases, a cable with a cross section of 1.5 sq. mm is enough. Due to the general trend of switching to LED equipment, there is no prospect of the need to increase the load capacity of the cable for light in any apartment.
For sockets
Enough for household outlets section 2.5 sq. mm. But for individual consumers (washing machines, air conditioners, etc.), it is necessary to provide individual lines with an increased cross-section of conductors.
Important! The cross-sectional area of the conductor depends not only on the load, but also on the laying method. Flush wiring has worse cooling conditions, so the tendency to overheat is higher, which means that thicker conductors must be chosen. This is taken into account in table 1.3.4 of the EMP.
Special cases of lighting arrangement
Separately, it is worth considering individual options for arranging lighting for non-residential objects. They have their own specifics.
Bath and bath
Washing rooms are characterized by high humidity, so it is forbidden to lay electrical lines in metal pipes and hoses because of their tendency to corrode. Steam rooms of baths and saunas also have an elevated temperature, and electrical wiring in them is allowed only with heat-resistant cables and wires:
- RKGM;
- PRCA;
- PRKS;
- PMTK.

You can also use foreign-made OLFLEX HEAT 205, but it is more expensive.
street lighting
Peculiarity street lighting in that the lantern(s) may be at a considerable distance from the switchboard and switch. Therefore, after choosing a standard size, an additional check must be done. It is necessary to make sure that at the calculated load the voltage at the farthest point will not be lower than the rated voltage by more than 5%. The easiest way to calculate voltage losses is through online calculators that can be found on the Internet. If the selected wire for light does not meet this condition, it is necessary to use products with a higher bandwidth.
Porch, gazebo or balcony lighting
In this case, the aesthetic component is of great importance. This means that any homeowner will opt for hidden wiring for lighting arrangements, with the possible exception of a retro design. This is not prohibited by the rules, but we must remember that this may require an increased cross-section of wires, which will be reminded by the same table 1.3.4 of the PUE. What if alcove stands far from the switchboard, you must not forget to check the line for voltage losses.

The choice of conductor products for lighting is a responsible matter. Failure to follow simple rules can cause a lot of trouble in the future. To avoid them, you just need to study the simple conditions of choice.
