Automobile lamps - types, marking, purpose and appearance
Lighting elements in cars and their fastening-contact systems vary depending on several factors:
- country of manufacture of the car;
- car brand;
- model year;
- purpose of the lamp in the design.
Thus, car lamp bases are not interchangeable, and replacing a burnt-out lighting fixture turns into a rather complicated process. You have to understand the designations, decipher the markings on a specific element, and even the same type of light bulb varies in performance. At the same time, the lack of a single standard opens up opportunities for motorists who want to not only replace the unit, but also upgrade their auto light, which is commonly referred to as “collective farm tuning”.
Light bulbs according to traffic police laws
Regarding the legality of such activities, everything is far from clear, since regulatory authorities prohibit interference in the design of the car. In principle, these measures are not groundless, because most drivers strive to achieve maximum illumination of the roadway, which is to the detriment of oncoming traffic drivers who are blinded by bright light. The situation is contradictory, since on the one hand, even a short-term blinding by oncoming headlights can lead to a loss of control, and on the other hand, insufficient illumination of the roadway also increases the risk of accidents. In practice, the only way to make the road in front of the car more visible at the moment of oncoming headlights is to increase the brightness of your own.
As a result, everything comes down to the pursuit of brightness, and some states, including the Russian Federation, are trying to regulate this issue at the legislative level, maintaining a single standard for the level of emitted light, the degree of side illumination and the presence of a clearly defined border between the central and peripheral light spots. However, according to statistics about 40% of all cars in the Russian Federation have lamps in the design of headlights that are not provided by the manufacturer cars. In most cases, this is not a reason for drawing up a protocol on violation of the rules by traffic police officers, since it is difficult to visually determine the discrepancy between the ED unit (operational documentation).
From July 1, 2021, in the Russian Federation, the legality of any changes made to the design of the vehicle that are not provided for by operational documents will be assessed by the traffic police using a laboratory method in accordance with GOST 33670-2015.This means that everyone can legalize their auto-tuning if the laboratory examination proves the safety of the changes made.
In the United States, crime bosses don’t bother with such issues, by the way, and they are allowed to drive with any lotions. In any case, even to install the original light bulb, you have to navigate the main types and modifications of car lamps, since the installation and fastening methods, as well as power sources for auto lights, are not unified.
Some historical facts
The first headlights for Karl Benz cars in 1985 were ordinary kerosene stoves.
By the end of the century, kerosene light sources were replaced by acetylene lanterns, similar to those of a locomotive, operating on the principle of a gas burner.
And only in 1910 on Cadillac and Rolls-Royce were installed the first headlights with a reflector familiar to everyone, powered by a battery and working on the principle of Ilyich's light bulb.
Since then, the electrical source of energy for lamps has remained unchanged, which cannot be said about the principle of their operation and design features that affect the main characteristics of lighting devices.
Types of automotive lamps
According to these criteria, there are several types of electric lamps used in the automotive industry.
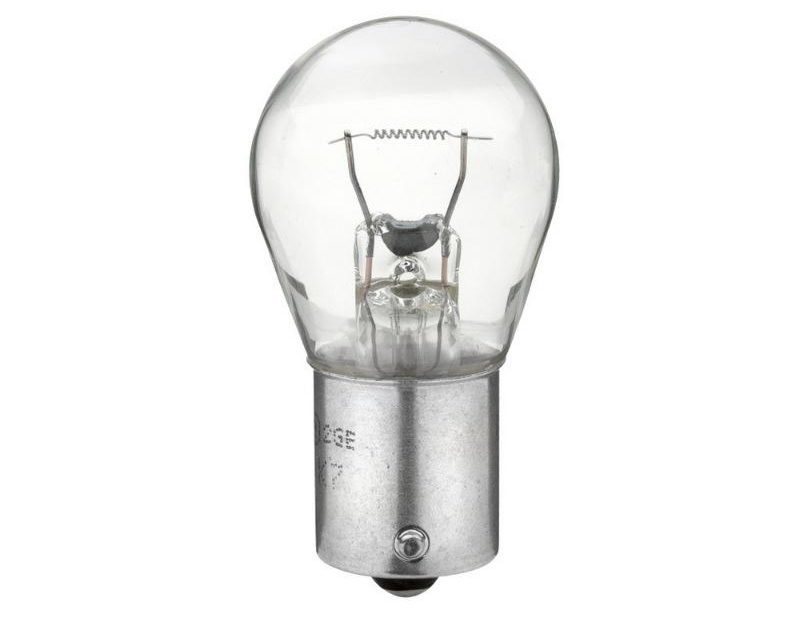
incandescent
They are a tungsten filament in a glass flask, from which air is pumped out as much as possible. When voltage is applied to the opposite ends of the filament, the tungsten is heated, accompanied by the emission of photons of light in the visible spectrum. Due to insufficient power and low resource, as well as the glow heat of up to 3200 K for headlights, this type of car lamp is used only in vintage retro cars.And in modern cars it is used to illuminate the interior and instrument panel.
Read also: Marking and decoding headlights
Halogen
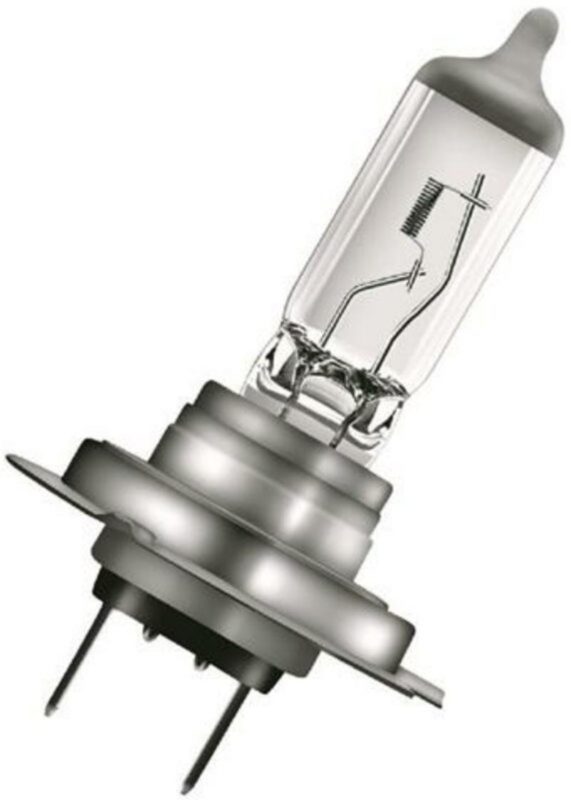
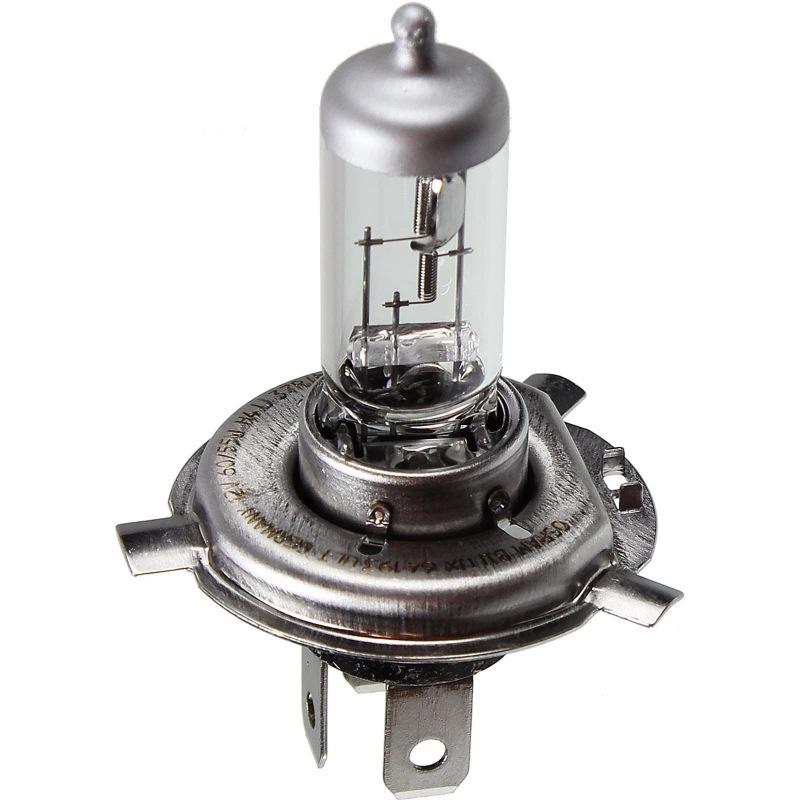
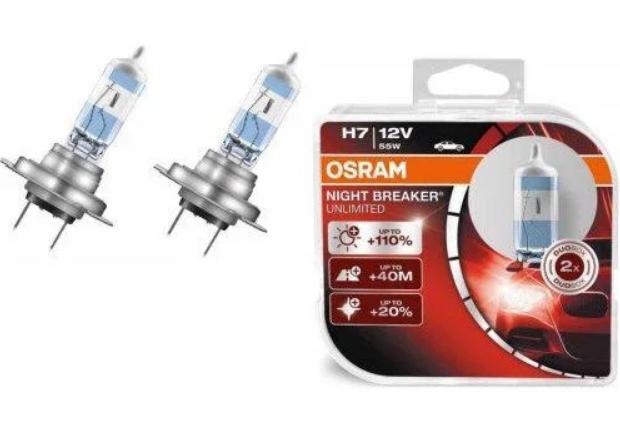
Modification of incandescent lamps, which consists in the fact that instead of a vacuum, bromine and iodine halides are pumped into the flask. These halogens prevent the vaporized tungsten particles from adhering to the inner surface of the glass. Actively moving inside the flask, these particles fall back onto the filament and weld with it under the influence of temperature. Thus, there is a partial regeneration of the tungsten coil. The process is still not infinite, since the evaporated particles settle in a chaotic manner, forming sections that are uneven in thickness, which ultimately leads to the filament burnout in thin gaps. For headlights, in addition to single-filament, double-filament lamps are used, in which the spirals are arranged in such a way that one serves for the low beam and the second for the high beam.
In addition to a doubled service life, halogens shine twice as brightly as conventional incandescent lamps, and such autolight is widely used to this day.
gas-discharge
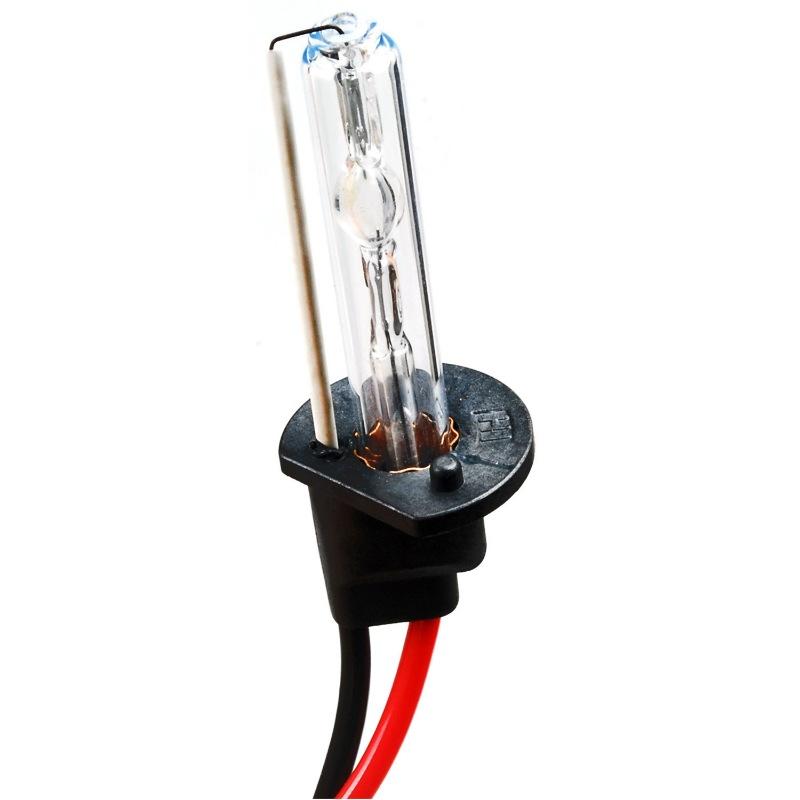
At the end of the last century, halogens were partially replaced by xenon lamps. Unlike their predecessors, these devices operate on the principle of an arc discharge in a gaseous medium. The flask of these lamps is made of durable quartz glass, xenon gas is pumped into the flask, and two tungsten electrodes with Invar spacers are soldered into it on both sides. When voltage is applied to the electrodes, a discharge occurs between them with the emission of photons of light. Since xenon itself forms a column of luminous plasma only near the cathode, mercury, sodium and scandium salts are added to the bulbs of autolamps.Due to this, the main stream of light is formed by a pair of salts and mercury, and xenon serves for the initial start-up and heating of the main elements. The light of such lamps gives a bright stream, with warmth up to 6000 K. It is these characteristics that attract car owners so much, but a special ballast is needed to start and operate gas discharges.
For headlights where separate optics are not provided, bi-xenon lamps are used - the same xenons, but installed in a special mechanism that regulates the focal length and direction of the glow. Headlights that do not have such a mechanism are unable to switch between low and high beam modes with xenon lamps.
Read: 6 best models of xenon lamps
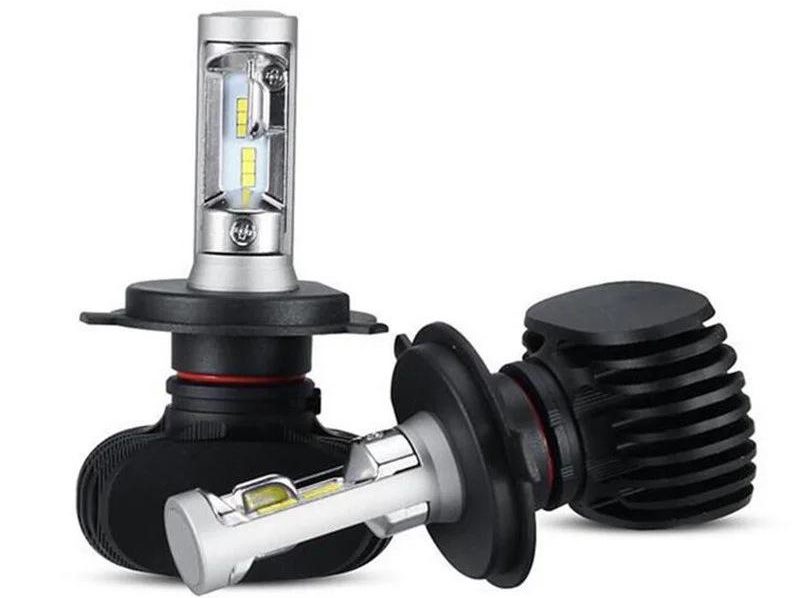
LED
The next step in the evolution of auto lighting is LED lamps. The light source here is a semiconductor crystal placed under a phosphor dome. The design of the lamp has a control circuit and a driver necessary for the operation of the LEDs. Since the LED elements and the driver get very hot, a massive heatsink is needed for heat dissipation. The crystals themselves are placed on both sides in the form of tracks imitating filaments. The upper track is responsible for the near, and the upper for the high beam, and both groups are covered with hemispheres that cut off direct rays so as not to dazzle oncoming drivers. These lamps have a life of up to 20,000 hours and the warmth of light in almost any required range, up to 8000K, which makes them the most durable and brightest of all analogues. The main disadvantage of LED car lamps is that they do not have light distribution along the entire radius of the reflector and lens, like halogen or xenon lamps. This results in two problems:
- Their installation is possible only in a strictly adjusted horizon, which does not always coincide with the design of the seat in the headlight.
- To realize the full potential of such devices, you need optics and reflectors originally designed for LED lamps.
The latest development based on LED technology is laser headlights. This innovation made it possible to increase the range of the headlights to 600 meters, but too narrow a cone of light and space prices for lasers have not yet allowed the novelty to fully spread on the autolight market.
Recommended: 7 best LED lamps for cars
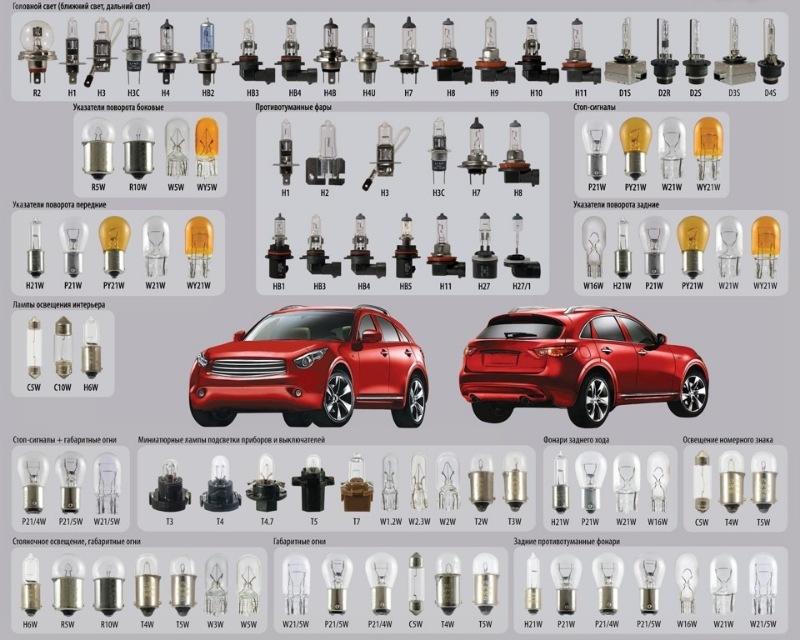
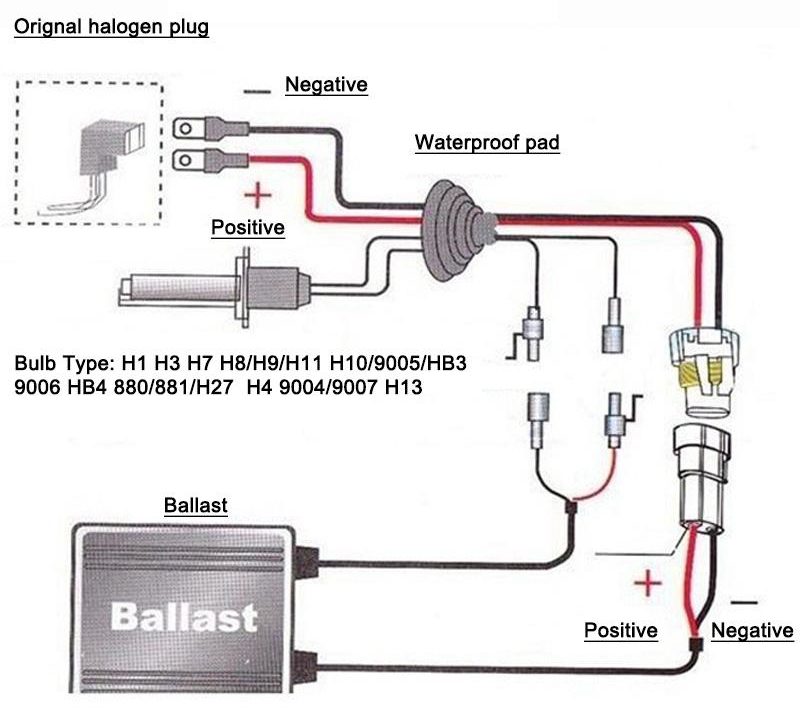
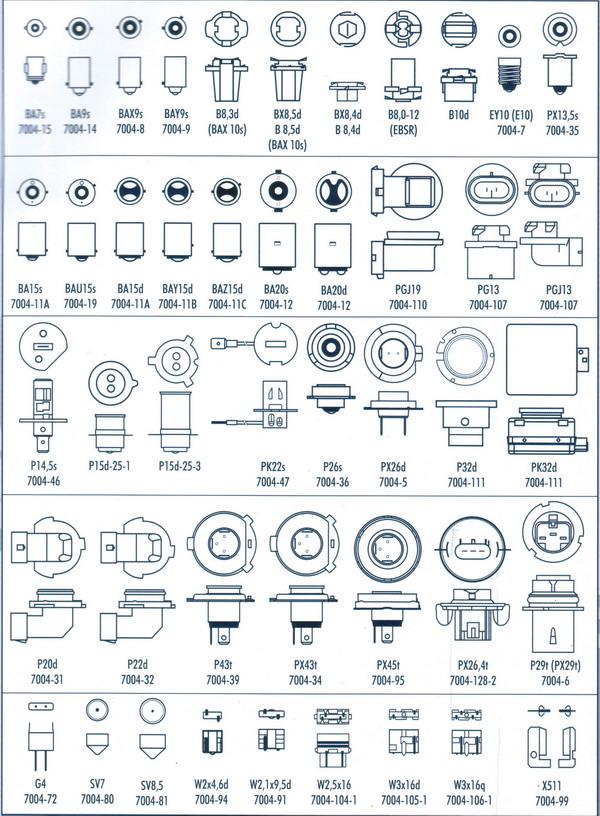
Types of car bases
To hold the lamp in its seat and seal the bulb, a base is needed that has contacts for connecting to a power source. Depending on many factors, plinths vary in shape and size of structural elements.
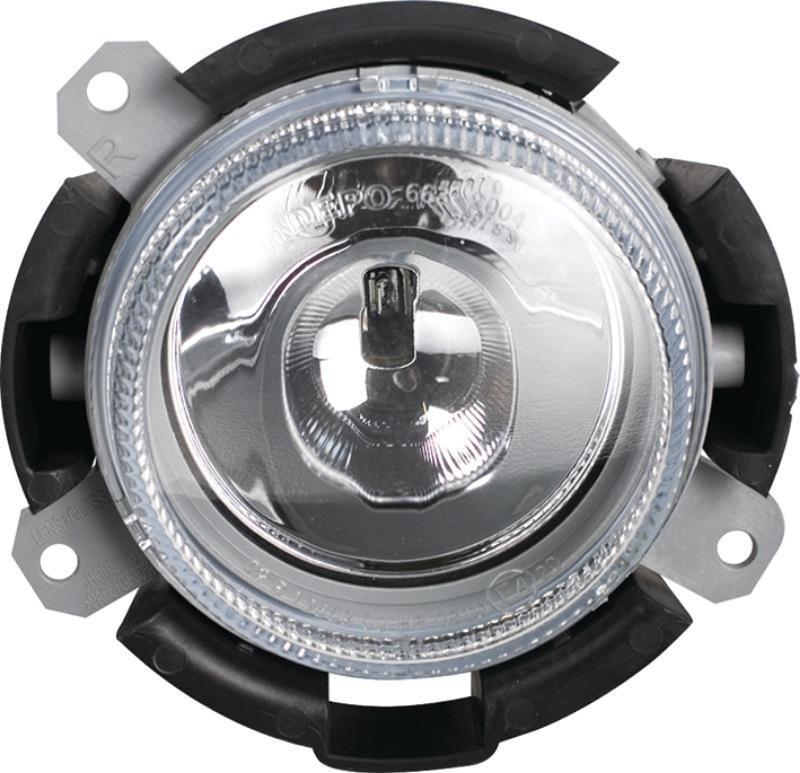
With protective flange
He's focusing. It is used in headlights, as the studs on the flange are located in exact accordance with the mounting grooves. This allows you to achieve the same focusing of the rays in the left and right headlights with a strict angle of inclination. Fastened with bolts or a clamping spring located at the rear of the headlight housing. In fog lights, a filament coil, a gas bulb or an LED panel are located perpendicular to the reflector. Contacts are connected using terminals.
Soffit
They are shaped like voltage fuses. This arrangement of plinths allows these light sources to be installed in flat structural elements. They are used to illuminate the license plate, dashboards, interior, trunk.
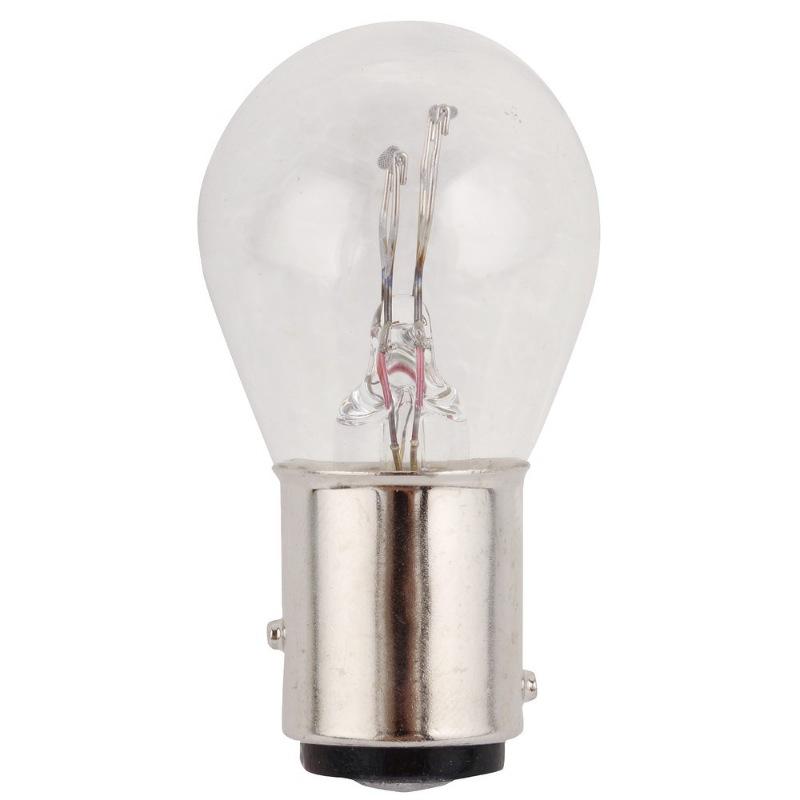
pin
They are bayonet. Similar to threaded, but the thread function is performed by one or more pins.The pins can be offset in height and radius. Fixation occurs by turning the lamp 10-15 degrees clockwise until it stops. The metal case of the base and one or two solderings on the end serve as a contact. It is used in all types of lighting, except for the head light, most often for direction indicators, brake lights, parking lights.
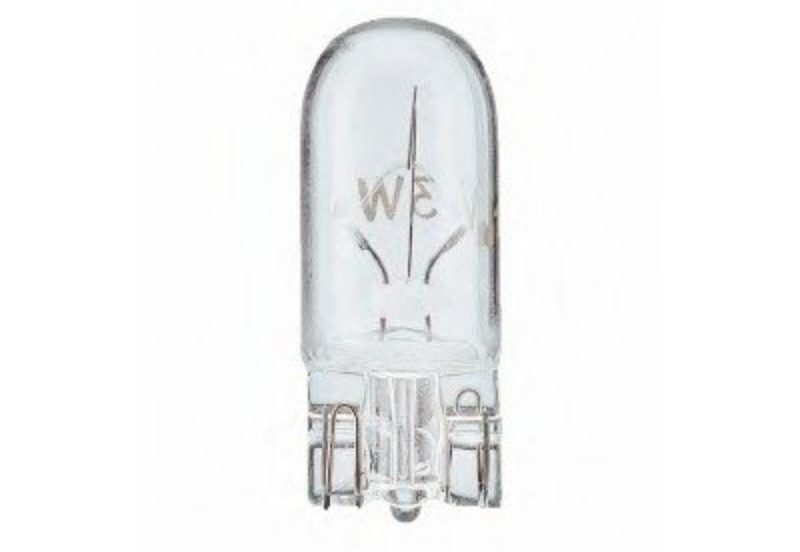
With glass base
There are no metal fasteners in such a lamp, and retention in the seat occurs due to fixation with a spring clip in the cartridge. They are installed in side lights, emergency lighting, dashboard lights and everywhere where high power is not needed.
New types of plinths
As such, there are no fundamentally new types of compounds that have received mass distribution yet. All manufacturers do is modify existing options, slightly changing the shape and location of fasteners in order to bind the consumer to a specific company and service in the company's car services. An example is the socles H4, H7, H19 in which there are practically no differences, but it will not work to install them in the same cartridge, since the protrusions on the flanges of these lamps differ in size. For some types of connections there are adapters, but their use makes the device more vulnerable to external influences.
Video: For which lamps manufacturers specifically reduce the service life.
Marking and designation of autolamps
By number of contacts
In some markings, at the very end, a small Latin letter indicates the number of contacts in the base according to the principle of the first letter of the Latin calculus:
- s (single) - 1;
- d (duo) - 2;
- t (tres) - 3;
- q (quatro) - 4;
- p (penta) - 5.
An example is the common P45t base, where the letter t means that the bulb is powered by three pins.
By type of base
According to GOST 2023-88, adopted back in Soviet times, the labeling of lamps does not always contain information about a specific type of connecting system. For example:
- ACG - an abbreviation meaning that the device is an automotive quartz halogen lamp;
- BUT - a letter informing only about the belonging of the lamp to the vehicle;
- AMN - an autolamp, where the letters MN indicate miniature sizes;
- AC - the only case in which the letter C denotes a soffit base.
With the ECE European standard, things are somewhat better. Here, separate designations have already been allocated for maximum information content of all design features of the lighting device, where:
- H - halogen lamp;
- T - miniature;
- R - standard with a base diameter of 15 mm.
With regard to a specific type of base, according to the European marking, there are:
- P - flange;
- W - glass;
- BA - bayonet, with symmetrically located pins;
- BAY - bayonet, with pins shifted in height;
- BAZ - bayonet, with pin offset along the radius and height;
- G - pin;
- E - threaded.
If the lamp is made in the USA, then the American DOT standards provide for the following designations:
- HB1 and HB2 - halogen, double-filament lamp;
- HB3 — single-filament high beam;
- HB4 — single-filament dipped beam;
- D1R, D1S — gas-discharge, the first generation;
- D2R, D2S — gas-discharge second generation.
Letters S and R indicate the lens and reflex type of optics.
by color
In the abbreviation for the color of the flask, there is only one designation - the letter Y, from English yellow, informing about the yellow color of the lamp, for example, WY5W.
All other modifications are indicated by the company directly in the device model name, for example, Whitebeam III, CoolBlue, etc.
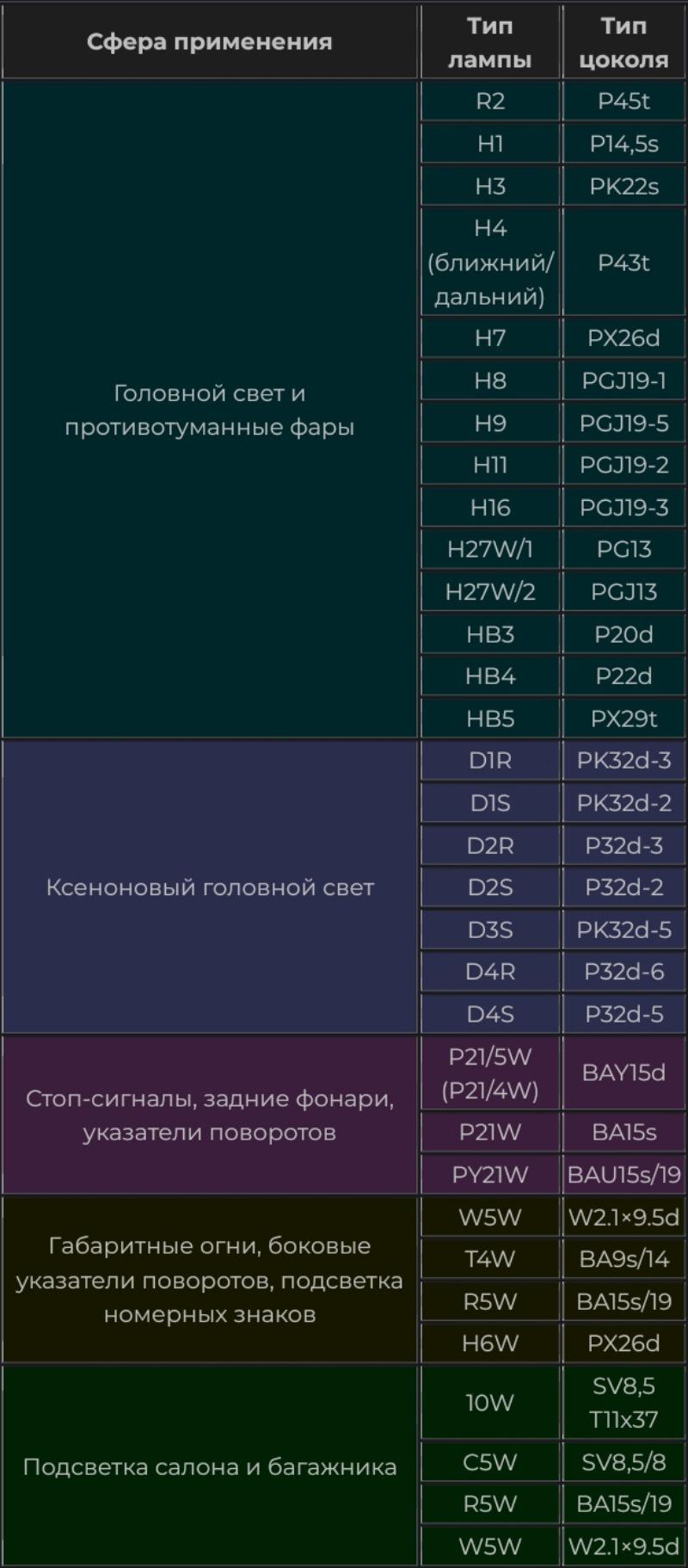
Table of compatibility of socles and car lamps
However, in lamps H and HB each type has the corresponding dimensions, in which the radius of the bulb and base is strictly regulated. Dimensions are shown in the picture.