What should be the distance between the lampposts
The distance between lighting poles is selected according to strictly established standards of GOST and SNiP. To determine the exact indicator, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors, so it is worth analyzing them in order to understand how the calculations are carried out. The illumination of the road and traffic safety depend on the correct location.

General features of determining the distance on the highway and in the city
The distance from one pillar to another is called the span. It varies depending on a number of conditions, so there are no clear rules that can be followed everywhere. First of all, you need to consider the following:
- Which area is illuminated. It can be a highway with different traffic intensity, city streets of different widths or park areas. The rules for each type are different.
- Type of poles and their height. Here it is important not only the distance from the lantern to the ground, but also the number of ceiling lamps on the support, their location relative to the roadway, etc.
- Type of light sources and characteristics of the lamps used. Very often, after replacing the lamp, the illumination changes if a variant with other characteristics was used. Therefore, calculations are always carried out for specific equipment in order to replace failed lamps with the same ones.
- The location of the pillars relative to the illuminated areas. It is important to observe the norms here, since it is impossible to put the supports too close, and if you move them far, the quality of the light will decrease.
- terrain and other features that can affect the illumination. For example, on the descents and ascents, you need to place the lights so that not a single area is left without light and at the same time the luminous flux does not hit your eyes.
- Pillar layout. The illumination of the roadway directly depends on this.
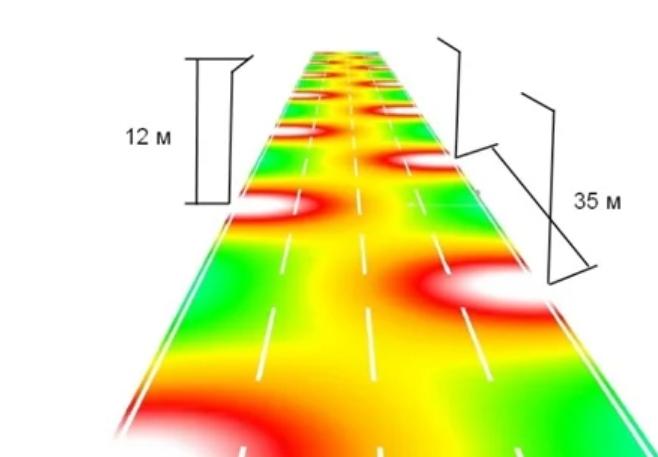
You can improve lighting by replacing lamps with more powerful ones or by using ceiling lamps with more efficient options.
Norms according to GOST and SNiP
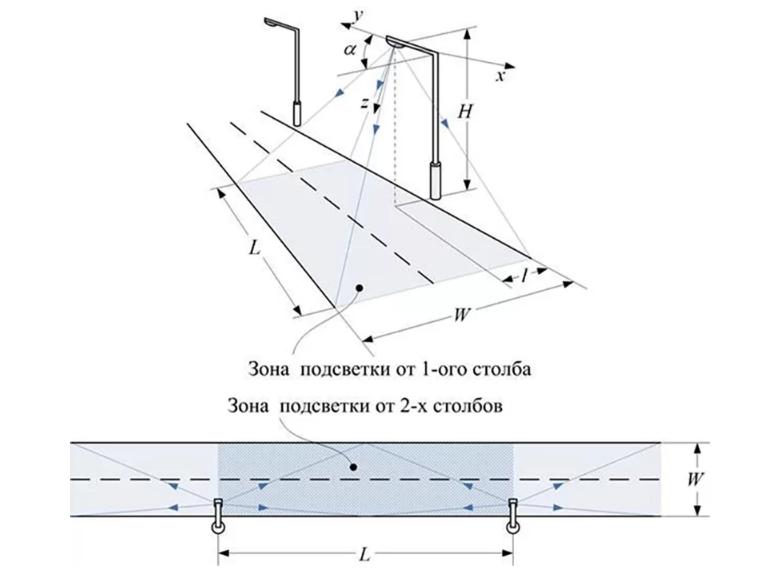
Building codes allow you to accurately determine all the parameters in order to choose the right location for lighting. In addition, there are a number of other aspects that need to be taken into account. They are shown in the diagram for clarity:
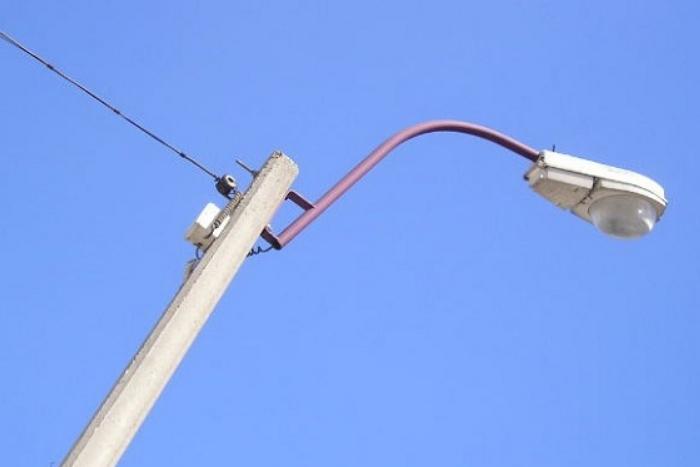
- Location height lighting plafond over the roadway. The higher this indicator, the wider the light spot, but the lower the intensity of illumination. Usually the height is marked with the letter H, it is selected for a specific road, the average is 9-12 meters.
- span width. The standard is determined based on the type of road, its lighting category and traffic congestion. It can be from 30 to 65 meters, so it depends on the correct calculation how many pillars will have to be installed in a particular area. The width on the diagrams is marked with the letter L.
- The position of the lighting dome regarding the roadway. To improve performance and provide illumination of the road, and not the curb, the luminaire is usually carried out using brackets of a suitable size. They can be included in the design or fixed separately in the upper part. This indicator is denoted by the letter I.
- Roadway Width - Another important factor that is repelled when determining the placement of lamps along the road. If the figure is up to 12 meters, you can put the lights on one side, if from 12 to 18, it is best to place them on both sides of the road in a checkerboard pattern. For carriageways with a width of 18 to 32 meters, a rectangular chess pattern is used. The indicator is denoted by the symbol W.
- Canopy tilt angle relative to the roadway, it is also necessary to select individually, since it depends on how the luminous flux will be distributed. It is marked with the symbol α and measured in degrees. By changing the angle, you can accurately set the lighting and adjust it if necessary.
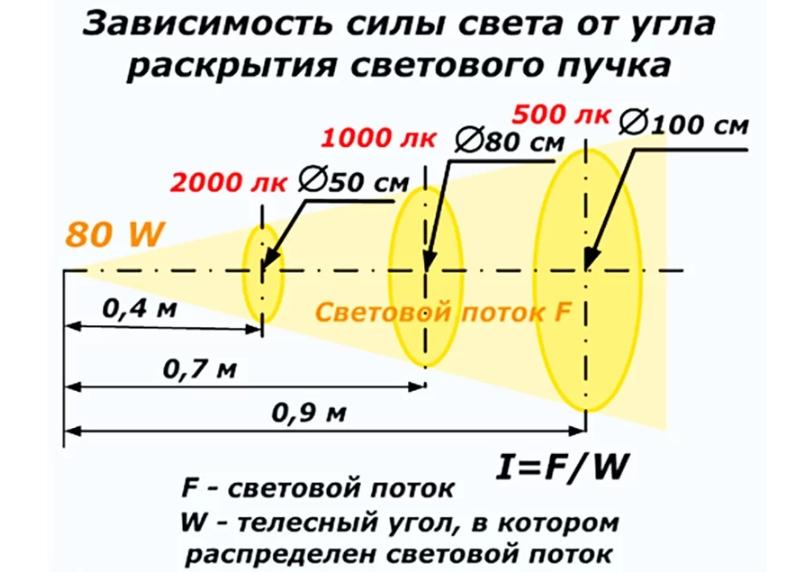
When determining the distance between the lanterns, the intersection of the light cones of adjacent lanterns is taken into account first of all. It is in these areas that the level of illumination is measured and checked for compliance with the standards.Since these are the most dimly lit parts of the roadway, they are taken into account by the regulatory authorities. Below is a table of indicators for fixtures with sodium lamps, one of the most popular today.
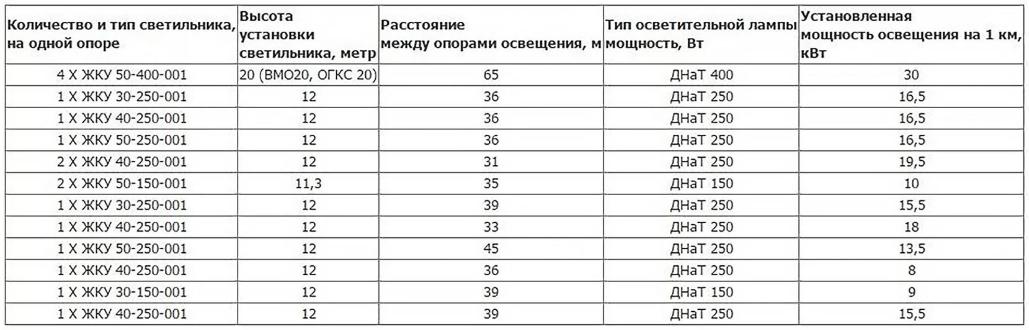
The main factors in determining the span between lampposts
The requirements for road illumination are prescribed in GOST R 54305-2011 (clause 4.1). The main indicator that affects the determination of the distance and other important points is the horizontal illumination. And it depends on the category of the object for lighting:
- Category A - These are highways and large city streets. The values depend on the intensity of traffic on the road, if it is more than 3000 vehicles per hour, then the average horizontal illumination should be at least 20 lux per sq.m. With an intensity of 1000 to 3000, the norm is the same - 20 lux, and if from 500 to 1000 cars pass per hour, then you need to focus on an indicator of 15 units.
- Category B - main roads of regional significance and objects equated to them. If the traffic intensity exceeds 2000 per hour, the horizontal illumination rate is 15 lux. It is also used for an average passage of 1,000 to 2,000 vehicles. When loading up to 1000 vehicles up to 1000, the indicator should be 10 lux.
- Category B - streets and roads of local importance in cities, the largest group. If the density of the traffic flow is over 500 cars, then the norm is 6 lx.For roadways with up to 500 cars per hour or much less, a horizontal illumination of 4 lux is sufficient.

The distance between lampposts located on one side of the road, in proportion to their height, is 5:1. If a checkerboard arrangement is used, the proportion increases to 7:1.
Support material
Used poles must be selected according to the standards of GOST 32947-2014. When choosing, the seismic features of the region, the minimum temperatures in winter are taken into account. The impact of aggressive environments should not be overlooked.
metal poles
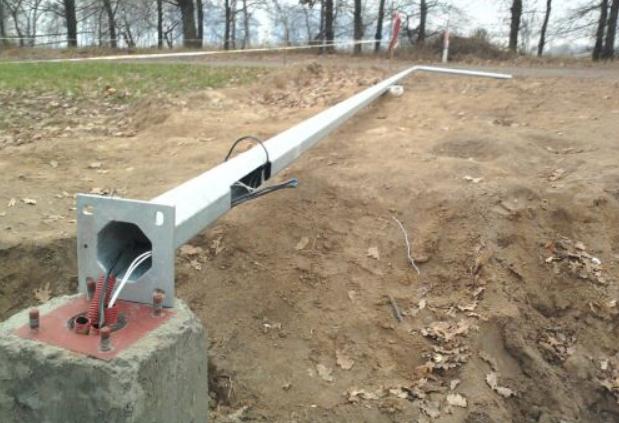

Steel is used to make this option. Suitable only for regions in which winter frosts do not exceed -40 degrees. Metal poles have the following features:
- Most often, two or 3 elements are connected by welding. But at a low height, there can also be solid supports that are installed by a crane.
- Metal poles can only be used for lighting, in which case they are called non-power. If the design is used to install wires and serves as a power line, the supports are called power.
- The cross section of the profile can be round or multifaceted. In some models, the thickness of the column is the same throughout its height, and in some it decreases, giving it a conical shape.
- According to the installation method, straight-rack and flange types are distinguished. The first is installed in the traditional way, digging a hole of the desired depth and concreting the base. The flange type is more convenient due to the fact that the base is poured in advance and a mounting flange is placed in it.It is necessary to install the post so that the holes coincide with the studs and tighten the nuts.
The metal is durable, but is severely damaged by corrosion, so anti-corrosion paints are used for the poles, the coating is updated every few years as it wears out.
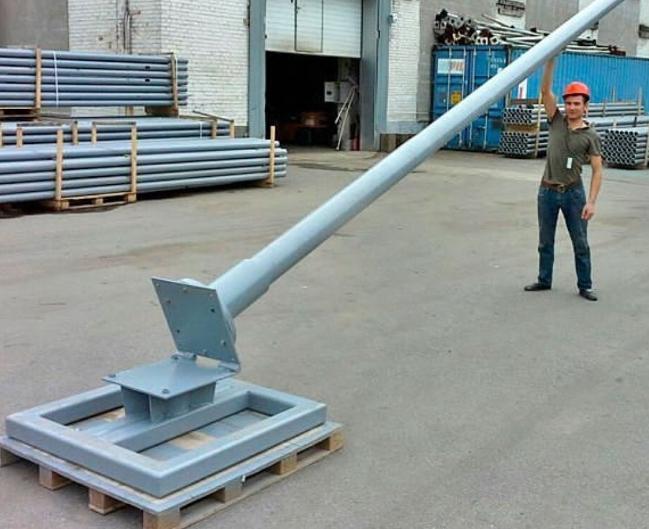
Reinforced concrete supports

The most common solution, as it has a long service life and does not require special care during use. The surface does not need to be cleaned of rust and painted. Features are:
- For production, vibration equipment is used, which compacts high-grade concrete so that no air bubbles remain inside. For reliability, a frame of welded reinforcement is inserted inside.
- Designs can be used in regions with temperatures up to -55 degrees. They are suitable for almost all areas, because they can withstand seismic shocks up to magnitude 7.
- The resistance to icing and strong winds of reinforced concrete is also an order of magnitude higher than that of metal poles.
- The shape can be different: pyramidal, round, conical, prismatic. Each of the options is designed for certain conditions, so you need to select according to lighting requirements.
- Mounting methods are the same as for metal supports. You can concrete the lower part in the ground, or you can use the flange method of fastening. In terms of weight, this option is much heavier, so appropriate equipment is needed to install it.
Concrete supports can be used for fastening wires. In the private sector and on streets with little traffic, this option is most often used.
Composite poles

A modern solution that is used more and more every year. It differs from traditional poles, but it has many advantages:
- They are made from polymer resins or other compounds. To give rigidity and ensure the desired shape, the products are reinforced with fiberglass.
- The poles are much lighter than concrete and metal poles, which simplifies transportation and installation. At the same time, they have a long service life - tens of years and do not require corrosion protection and renewal of the protective coating.
- Profile and dimensions may vary. All products are certified, there must be documentation for compliance with the requirements.
- The supports are suitable for both lamps and wires, so they can be power ones.
- Fastening is most often done in a flange way. But there are options that can be concreted in the ground.
The distance between street lights is not the only criterion for their installation. You also need to take into account several requirements for the location of the pillars. It depends on where it is better to lay the cable and what kind of extension of the lantern from the support should be used. Remember the following restrictions:
- There should be at least a meter from the pole to the curb if a freeway or a city highway with a large flow of traffic is illuminated. This is the minimum figure, it can be done more, but it cannot be reduced. This also applies to other rules.
- On most city streets, the minimum curb clearance is 50 cm. This applies to minor roads and other low traffic options.
- If the movement of trucks is prohibited on the roadway, then the smallest distance should be 30 cm. This option is used where there is no risk of damage to the supports by large vehicles.
- When lanterns are installed on the dividing strip, its width must be at least 5 meters. In this case, each support usually has two shades on each side.
- For parks, residential areas and recreation areas, the distances and the location of the pillars are selected individually. There are no strict rules here, it should be based on safety considerations so that the supports do not interfere.
- If there is no curb along the edge of the carriageway, then the minimum distance to the pole should be 1.75 meters.

If poles are installed in residential areas, then there must be at least 1 meter from the pole to balconies or windows. And it is better to make the distance even greater to eliminate any danger.
When installing poles, a number of criteria must be taken into account in order to ensure good visibility and create a safe system. The main indicator is surface illumination, so the distance between the poles, their location, the height of the lantern and its power are selected so that the system meets the standards.

